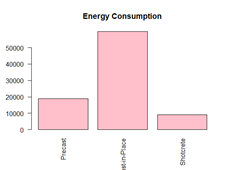
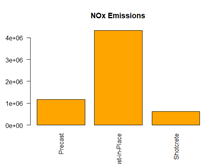
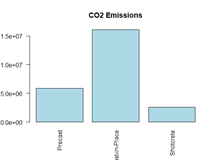
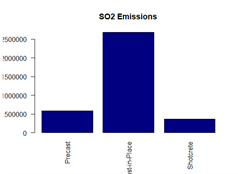
In this assignment, I conducted a Life-Cycle Assessment (LCA) of tunnel lining systems in road tunnels, focusing on their environmental and economic impacts. The study aimed to evaluate three design alternatives: Precast Concrete Segmental Lining, Cast-in-Place Concrete Lining, and Shotcrete Lining. The evaluation considered each option’s material efficiency, energy consumption, cost, and emissions.
The analysis covered the entire life cycle, including material extraction, construction, operation, maintenance, and end-of-life processes. Each option presented unique advantages: Precast Concrete Segmental Lining provided high precision and durability, Cast-in-Place Concrete Lining offered adaptability for irregular geometries, and Shotcrete Lining allowed for rapid application in complex shapes. However, trade-offs were observed in energy use, emissions, and long-term sustainability.
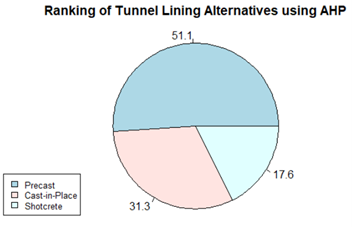
To determine the most sustainable alternative, I applied Multi-Criteria Decision-Making (MCDM) using the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP). This method assigned weighted importance to environmental and economic factors, ultimately ranking Precast Concrete as the most balanced option. The study emphasizes the importance of integrating systematic assessment frameworks to optimize infrastructure solutions for sustainability and efficiency.