Civil engineering systems such as a wooden or steel frame, runway pavements and seatings from a hangar are designed for a very long lifetime. These products serve as supporting infrastructure for private and business transactions of our society. Various factors such as daily usage, weather conditions and severe events (such as earthquakes, floods or landslides) and their combination contribute to systems deterioration and sometimes to their failure.
The airport system we are investigating, includes a runway and a hangar with footage.
Maintenance is very important to ensure safety operations. The system is close connected: physically and dimensional dependent. We define our system as a static inflexible system. One day of not operating costs the airport company 130.000$. Therefore the maintenance interventions will take place at the same time, to keep intervention duration as low as possible.
After running our algorithm, we will find out the total amount of days the airport has close for maintenance work.
For that we took four different system design under investigation and let them automatically find the lowest possible duration within their time range and maintenance duration.
In our scenarios, the frames of the hangar can be built of timber or steel and the pavement of the runway with either Hot mixed asphalt or portland cement concrete.
In the following, we are showing the advantages and disadvantages of the systems under maintenance effort. The footages of the frames are always the same but are from special concrete and need extra caring:
Timber Frame : Painting: every 10 – 25 yrs; replacement of single components: every 5 – 10 yrs;
Steel Frame : Painting: every 15 – 30 yrs; replacement of single components: every 20 – 30 yrs;
PCC Runway : Joint sealing: every 12 – 20 yrs; Small repair: every 8 – 18 yrs
HMA Runway : Joint sealing: every 8 – 16 yrs; Small repair: every 7 – 14 yrs
Bottom1 Footage : Cosmetic maintenance concrete bottom plate (EMC): every 5-10 yrs; Inspection measurement (IM): every 5 – 15 yrs; Concrete maintenance point foundation via injection (CMF): every 10 – 20 yrs; Replacement deck layer (RCBP): every 35 – 45 yrs; Replacement concrete foundation (RCF): every 45 – 55 yrs.
(The duration is roughly estimated by a third of its annual sequence in days)
The lifetime of the airport is 100 yrs.
1. Scenario
Timber Frame and PCC runway : 199 days closed for maintenance
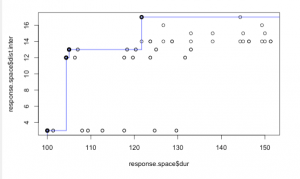
2. Scenario
Timber Frame and HMA runway : 199 days closed for maintenance
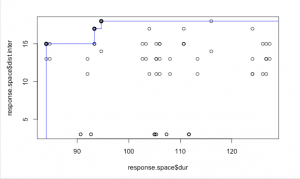
3. Scenario
Steel Frame and HMA runway : 199 days closed for maintenance
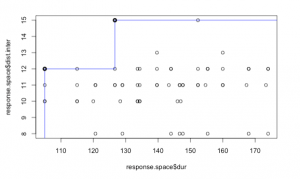
4. Scenario
Steel Frame and PCC runway : 199 days closed for maintenance
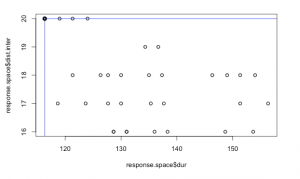
Conclusion: Every scenario shows a total time of duration for 199 days. This is owed by the many different inspection sequences and the long lifetime of the system. Also the duration is roughly estimated by taking a third of the sequencer number of the interventions.
If the maintenance duration is the same, we will decide to take a deeper look in the LCA for the steel frame with a PCC runway and a timber / HMA combination.