
INTRODUCTION
Cable car structure
There are many kinds of cable cars, and the cable car I’m mainly working on here is actually called Gondola lift. It is a more energy-efficient and environmentally efficient means of transport than the previous Aerial Trams. The following diagram can help us understand the mode of operation and the difference between the two cable cars.
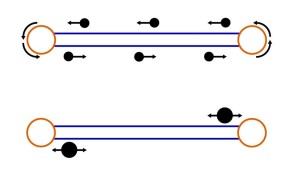
Figure 1 A simplified diagram comparing how detachable Gondolas and Aerial Trams operate: (Top) Small vehicles in a gondola system constantly circulate. (Bottom) Larger Aerial Tram vehicles shuttle back and forth.
Cable car accident
In order to better determine the failure mode of the cable car, I investigated the major cable car accidents in China and abroad. Four major accidents are worth mentioning. Below I will clearly display the date of the accident, the location of the accident, the cause of the accident, the number of casualties and other important information.
Table 1 Cable car accident analysis
| Location | Date | Cause | Number of casualties |
| Singapore | 1983 | (Human factors) Accidental collision | Seven people were killed and 13 were trapped |
| Tbilisi | 1990 | (Human factors) the hauling rope broke | 19 deaths and at least 42 injuries |
| China | 1999 | (Human factors) the hauling rope broke | 14 deaths and at least 22 injuries |
| Italy | 2021 | A lead cable broke and the emergency brake failed | 14 deaths and one child was seriously injured |
Possible failure of the cable car
The safety performance of cable cars depends mainly on the reliability of the wire rope. But there are many reasons for the broken wire rope, there are human reasons, such as construction failure, overload operation and so on, and those natural causes that we cannot predict, such as corrosion.
I also looked up a Chinese graduation thesis, which described a few important related information, summarized as follows:
Gripper:
The wire rope is subjected to concentrated wear (frequently check the changes in the joints and apply anti-corrosion oil once a week; the installation position of all rope grips can be adjusted in a certain direction every two months to equalize the force on the entire wire rope to avoid Concentrated wear of the rope grip)
Rope support wheels:
The lining will produce wear (when the lining wears two-thirds thickness, the wheel lining should be replaced in time)
Wind:
It is a major factor affecting the safe operation of the ropeway, will cause the carriers in the line to produce violent swings, In particular, lateral swings can easily cause carriers to collide with brackets. Therefore, the canyon area is generally equipped with wireless wind gauge.
emissions analysis
We considered an emissions analysis of a material from production to recycling, taking into account common and important environmental issues such as energy consumption, greenhouse effect potential (GWP) and Acidification potential (AP) and Eutrophication potential (EP). From the engineer’s point of view, this analysis is very comprehensive and conducive to our better choice of solutions. In the past, we only selected materials according to the force situation and the bearing capacity of the structure, which was often partial and one-sided. We only considered the material from which construction began, without considering the long-term effects of that material, post- recycling and replacement issues. Such an analysis is a superfluous task for the current engineers, but for Party A, it is indeed a measure with good long-term benefits, and I believe that Party A is also willing to pay for it.