Solar Power Tower Plant
A Solar Power Tower Plant (TP) consists of a central tower, which is surrounded by a field of flat, moveable mirrors, so-called Heliostats. These are arranged in a circle or semicircle around the tower and aim to concentrate and reflect the incident sun rays to a central point, the so-called receiver. It absorbs the concentrated sun rays causing high temperatures and thereby the heating of a heat-transfer-medium (HTM) as water, air or molten salt inside the receiver. Here, the transformation of solar energy to thermal energy takes place. By means of a conventional steam power plant this thermal energy is processed to electrical energy in a sustainable way.
Fig 1.3.1 : Central Tower and field of Heliostats of the Gemasolar Power Plant Sevilla, Spain
Within the system of a TP, the Heliostat resembles a very vulnerable component in terms of failure and efficiency loss depending on the environmental and technical circumstance as well as preventive actions to maintain the ideal initial setting. As Heliostats account for about 50% of investment costs, the optimization of this subsystem will derive ecological and economic benefits.
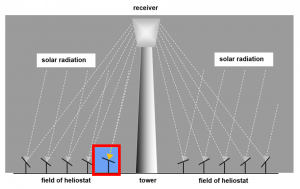 Fig 1.3.2 : Solar rays reflection
Fig 1.3.2 : Solar rays reflection
During a previous Life Cycle Assessment, the design option “Stellio” was figured out to be the most sustainable and efficient design option among two others. The focus of this assessment was put on the extraction of raw materials, the manufacture and construction of the Heliostat’s components as environmental impacts are considered to be small during the operation of a PT.
For the further analysis and optimization planning, the focus will be on the Stellio.
Fig 1.3.3 : Sun rays reciever
Other Integration Context:

