443Multi-objective formulations prove to be pragmatic models for various intricate engineering optimization challenges. In real-life scenarios, objectives often clash, making it challenging to optimize a solution for one objective without compromising others. A sensible approach to such problems involves exploring a set of solutions, each satisfying the objectives at an acceptable level without being dominated by any other solution. Genetic algorithms (GA) are widely employed for multiple-objective optimization, given their effectiveness in handling conflicting objectives inherent in many real engineering problems. These problems typically involve minimizing costs, maximizing performance, enhancing reliability, and similar conflicting objectives, making GA a suitable meta-heuristic for such challenges. (Abdullah Konak, 2006)
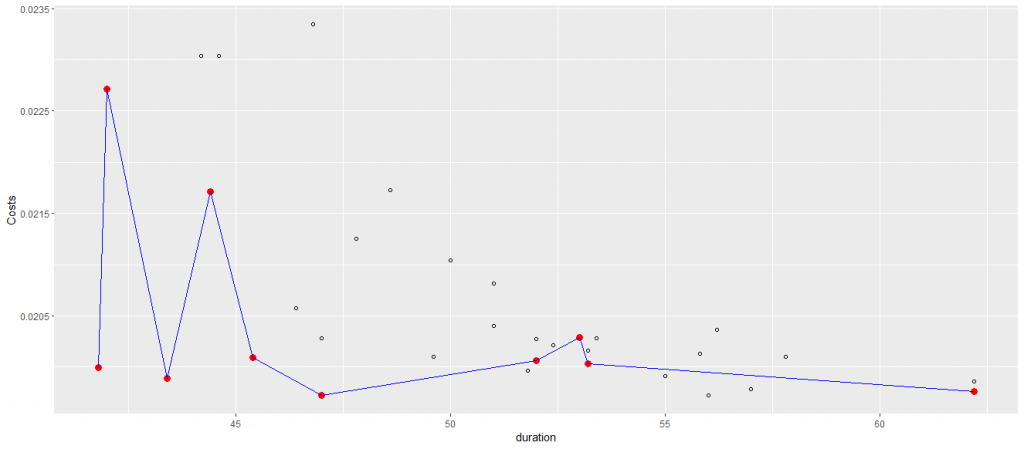
We implemented a genetic algorithm for the multi-objective optimization function that takes into account both the life cycle impact and the usability of the systems affected by maintenance tasks. Recognizing the dual influence of maintenance on both LCA and system usability is crucial for informed decision-making. This function incorporates energy usage and emissions into maintenance tasks. As an illustration, for pavement resurfacing, we assumed a 20% material application, impacting the system’s environmental footprint throughout its entire lifespan. The graph below illustrates the performance of various options, with the y-axis representing cost and the x-axis indicating the total duration of maintenance tasks. The alternatives marked in red outperformed the other dots on the graph, highlighting their superior performance in comparison to less favorable alternatives.
Figure 1 Pareto Front: Cost, Duration
The graph below outlines the maintenance ranges denoted by the red lines, illustrating the criteria used to achieve favorable scores across multiple parameters, such as maintenance duration and CO2 emissions.
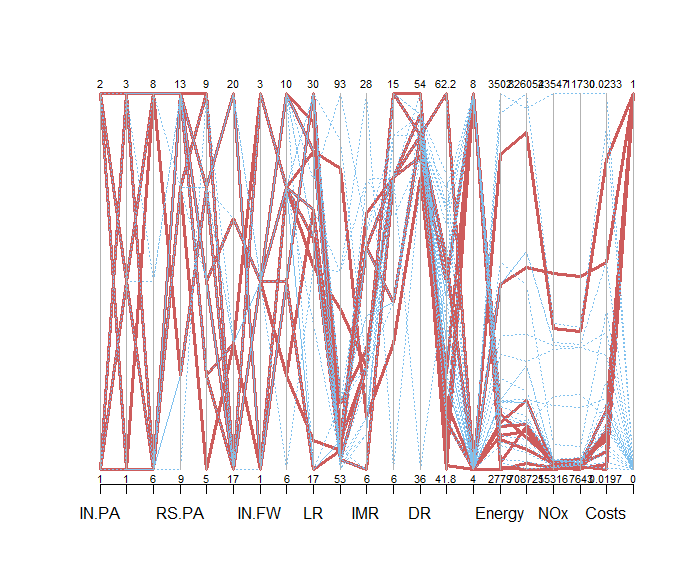 Figure 2 Pareto Optima: Design Parameter, Performance Criteria
Figure 2 Pareto Optima: Design Parameter, Performance Criteria