Introduction
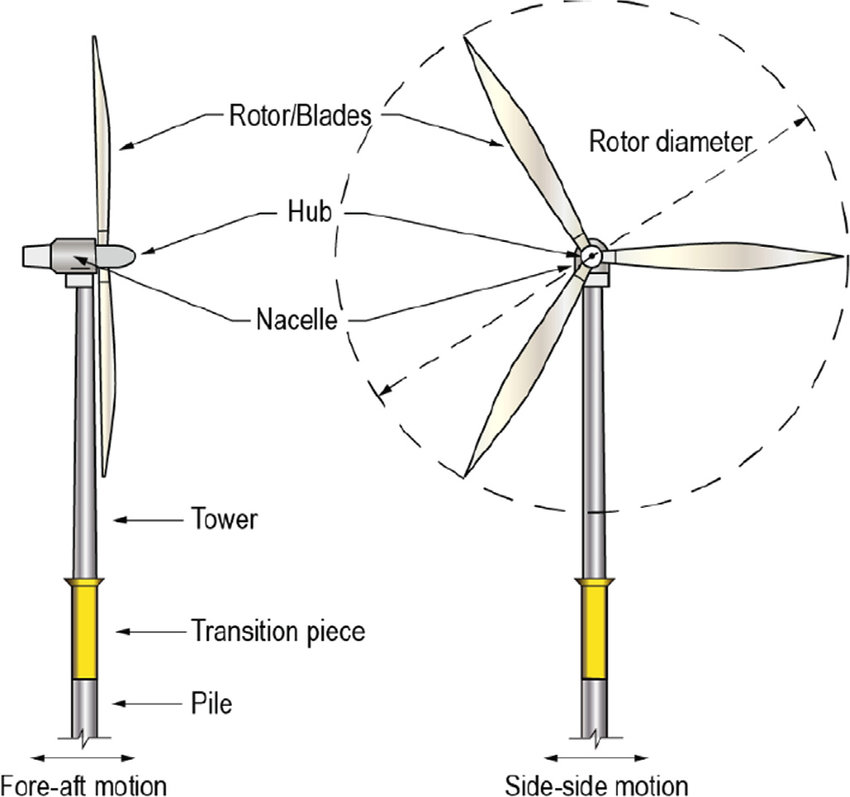
The Offshore Wind Turbines are one of the profoundly creating and requesting infrastructures in this modern world. They are typically conveyed in water bodies. When contrasted with the onshore turbines, they are shown to be more productive and calculated. Wind power is perhaps the quickest wellspring of renewable energy and they convert the sea’s immense breeze into 100 percent inexhaustible power. The designed average lifespan of an offshore wind turbine is approximately expected to be 20 years. The lifespan can go upto 22-25 years depending upon the maintenance and operations done throughout its lifespan. The wind turbine typically performs well before it reaches a critical condition and deteriorates after that stage. Decisions engineers make during the plan of a structural designed structure altogether affect all different stages.
Figure 1: Overview of an offshore wind turbine.
Goal and Scope
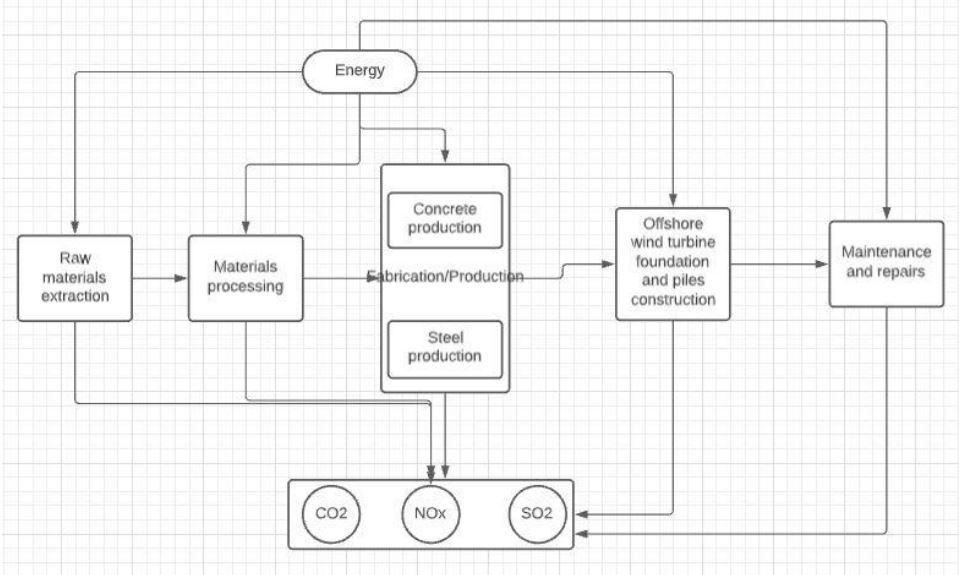
The main goal of the assessment is to carry out an analysis t0 observe its impact on the environment and surroundings. During the construction process and its lifetime the system is emits so many harmful gases that cause air pollution are considered for the study. These gases affect the tropospheric ozone and also affect the flora and fauna. They also contribute to the formation of acid rain and smog which affects the natural system and causes an imbalance in nature. The complete stoppage of the same is impossible but if we really care and pay attention we could decrease the amount up to a certain extent. The study is limited and doesn’t dive deep into the emissions caused by processes such as operations, transportation, dismantling, recycling, etc.
Figure 2: Scope and Boundaries of LCA.
Design options
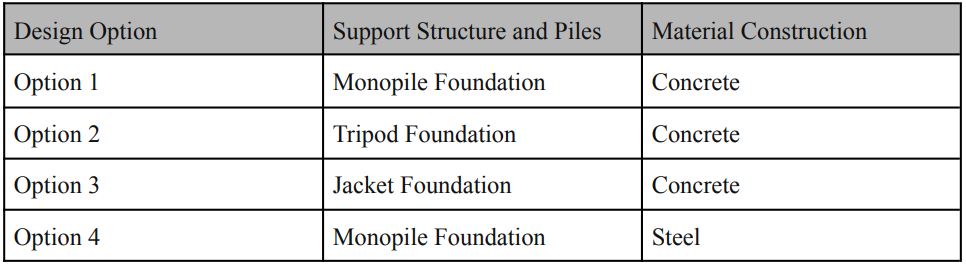
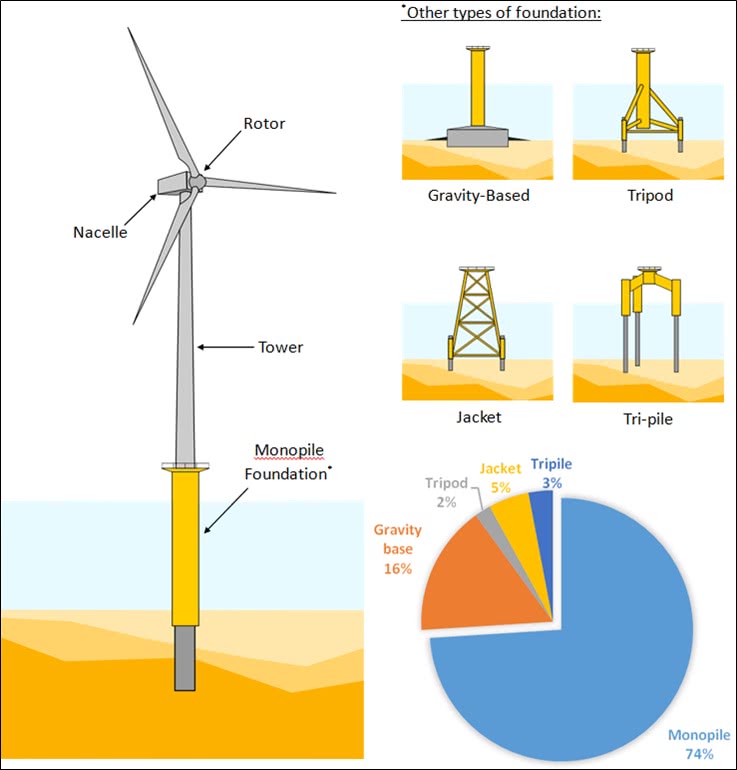
A total of four design options have been considered for the component. For these four design options, maintenance, support structure repair and pile repair have been done in the lifecycle of the system. Monopiles, Tripod and Jacket foundation have been considered for the design and analysis. The materials used for the construction of these foundations are concrete and steel.
Figure 3: Design options.
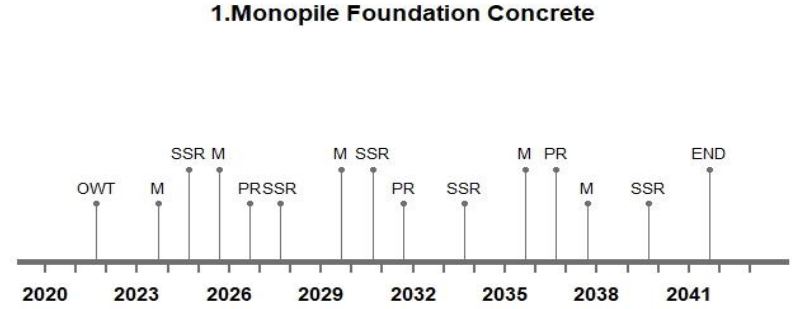
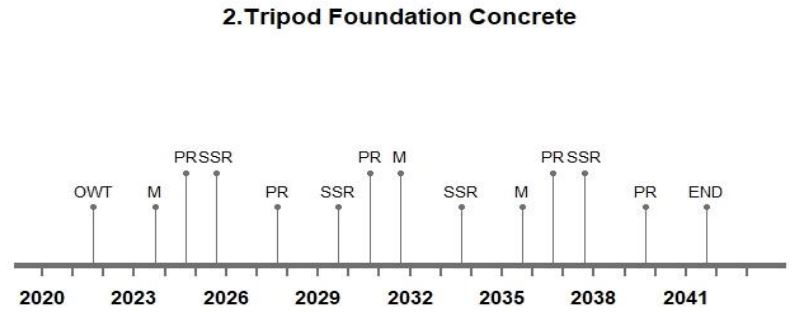
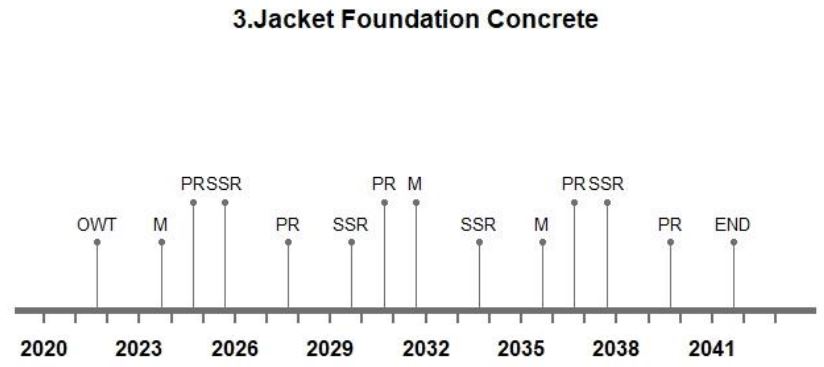
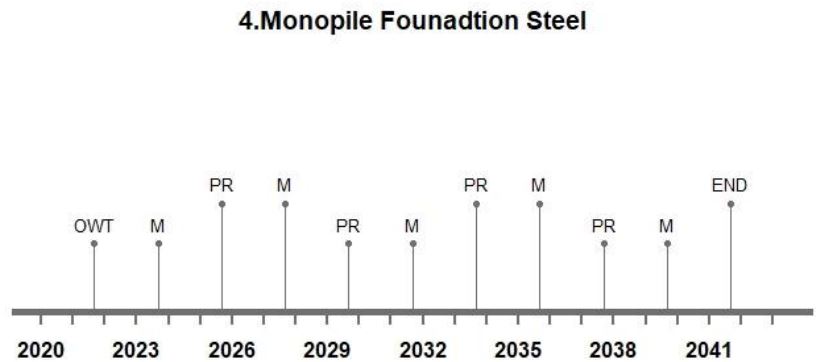
Life Cycle Timeline
The designed average lifespan of an offshore wind turbine is approximately expected to be 20 years. The lifespan can go upto 22-25 years depending upon the maintenance and operations done throughout its lifespan. The wind turbine typically performs well before it reaches a critical condition and deteriorates after that stage. The life cycle analysis includes maintenance, support structure repairs and pile repairs in respective years. The life cycle timeline for the mentioned design options are visualized below:
Figure 4: The life cycle timeline for different design options.
Life Cycle Inventory and Analysis
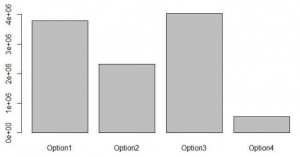
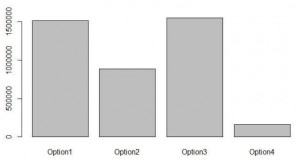
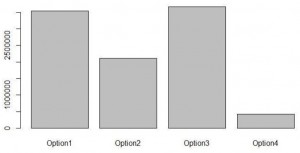
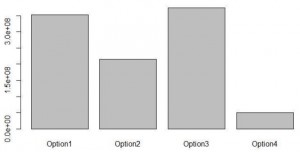
During the production and construction a lot of harmful gases are released into the atmosphere that pollutes and causes air pollution as well as water pollution. The results for the four design options for their emissions of CO2, NOx and SO2 and also the energy consumed are obtained. The foundations constructed using concrete and steel both emitted these hazardous gases in a certain amount. Some factors that affects the emissions are the selection of the materials for construction, the area of cross section and also the quantity of the materials used for the construction.
Figure 5: The emissions and the consumptions of the four design options.
Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis
With respect to various effect, the decision maker should concentrate analysing the multi-standards choice to have the option to pick the best design choice. Firstly, the score matrix ought to be characterized for every presentation measures, taking note of that the network should be characterized based on the degree of level of these models among the design options.
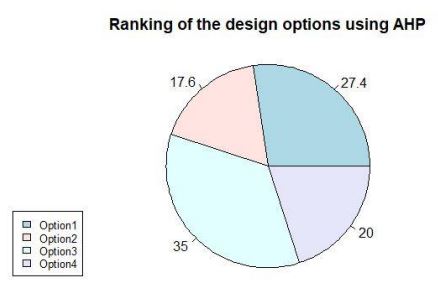
By simulating, the AHP results will obtained below:
Figure 6: Pie representation of the four design options using AHP.
From the pie charts obtained, it is clear that Option 3 has the highest value that is the jacket concrete foundation. The toxic gases emitted from both the materials steel and concrete were analysed and in the future, it should be taken care of during the construction of a new structure or system in order to create an eco friendly system.
References
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF 2-MW WIND TURBINE TOWER, UMESH K N et.al, BHARATH P et.al.
BWEA 2003 Proposed offshore windfarm locations. Map. London: British Wind Energy Association. (Available at http://www.offshorewindfarms.co.uk/sites.html.)
Border Wind Limited 1998 Offshore wind energy: building a new industry for Britain. A report prepared for Greenpeace. London: British Wind Energy Association. (Available at http://www.offshorewindfarms.co.uk/reports/gpbw.pdf.)
Wind Turbine Design, Performance, And Economic Analysis, James H. Sexton et.al
Life Cycle Cost Assessment of Offshore Wind Farm: Kudat Malaysia Case, Wesam et.al.
Other Systems:
Integration Context of the civil systems