Single Storey House
Single Storey House
A house is the simplest structure when viewed by a common man but it becomes a complex one from an engineer’s perspective. The most basic necessity or utility of a house is to provide shelter to its occupants. It maintains a comfortable and cozy environment, keeping the residents safe from the harsh forces outside. Apart from providing all the basic amenities for living like cooking sleeping etc. it also acts as a haven for people, which creates a sense of security as they have a place to call their own and return to.
In case of natural calamities like an earthquake, the same house which provided a sense of security suddenly becomes a monstrous thing that might risk the life of its occupants if a failure occurs. To reduce this risk of failure and to predict it, we carry out the Risk-based assessment of the system’s condition.
For a failure analysis, a house was selected as a domain whose deterioration model was formed with the help of the Markov chain. The total lifetime of the house was assumed to be 70 years, which was also assumed for a Life-Cycle Analysis. In the latter, the foundation of the house was chosen as a component with different design options to be analyzed. A comparison was made for all design options with the help of techniques such as life cycle inventory, life cycle cost analysis, and MCDM, which resulted in identifying the Isolated Footing as the best option.
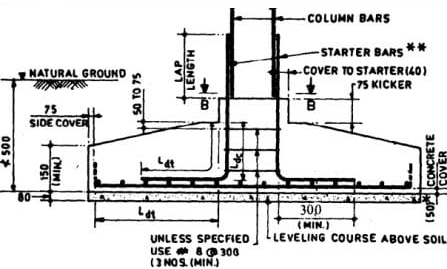
Isolated Footing
Isolated Footings, also known as spread footings, are a type of shallow foundation. They support individual columns of a house. There are two portions of this foundation, the reinforced concrete cement (RCC) section which forms the main structure, and the plain concrete cement (PCC) section which forms the cap at the end of the foundation.
Fig 1.4.1 : Cross section of a typical isolated footing
Following fixed values were also defined for Isolated Footings.
- depth of the isolated footing = 1.5 meters
- depth of the PCC cap = 0.1 meters
- factor for the isolated footing (RCC) = 0.03
- factor for the isolated footing (PCC) = 0.1
The reduction factors mentioned above are to be multiplied with the total volume of the integrated system, to get a realistic volume of isolated footing. The isolated footing does not cover the whole built up area as a single block and there is some spacing between the consecutive footings therefore the total volume needs a reduction factor.
Other Integration Context: