Definition
A green roof system is an extension of the existing roof. It is indeed an assembly of materials including plants added to a traditional roof system[1].
Green rooftop provides a number of social, environmental and economic benefits both in private and public. These benefits are summarized in the following table :
| For Public | For People | For Building |
| Stormwater Retention[2], Moderation of Urban Island, Heat, Improved Air Quality, Habitat Creation | Aesthetic, Recreation Time, Agriculture | Energy Saving, Fire Resistance, Prolonging life of waterproofing membranes, Sound Insulation |
Domains Requirements
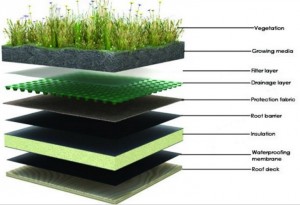
The Layers
- The layers are put directly on the roof desk.
- The first layer is the waterproofing membrane which protects the roof from humidity.
- The insulation layer isolates the roof thermally.
- The protection fabric and the roof barrier also protect the roof.
- The drainage layer drains the exceeding of water to avoid the roots to rot, the choice of this layer is function of the tilt of the roof.
- The filter layer holds the soils and the vegetation which could block the drainage.
- The vegetation will grow on the growing media.
The structural loading Capacity
Before the installation of the green roof the structural assessment must be checked. The structure must indeed support the weight of the green roof (more than 400 kg/m² for an intensive green roof).
Vegetation
The choice of vegetation depends of the climate, the exposition of sun, wind and the use of the green roof. The vegetation will also influence the need of maintenance (some vegetation need more maintenance than other) and the depth of the growing media. Vegetation is a main domain of a green roof top and the main benefits of a green roof top is due to vegetation.
Water system management
An irrigation[3] system and a drainage system need to be installed. The drainage system is indispensable to deal with extreme rainfall events or flooding. The irrigation system has to be designed considering the purpose of the roof, the substrate water storage, the water availability, the vegetation, climate and water pressure. For instance, the irrigation system can be a recycling system, a drip irrigation system or a sprinkler system.
The research lead to the creation of this ontology : Green Rooftop Ontology .
The parametric Model
Green Rooftop Parametric Model
Design Challenge
One of the main challenge of a green rooftop is to ensure that the building or the structure will support the added weight. This weight is influenced by the volume of the layers, so by the surface (created by the geometry) and the thickness. The thickness of the layer is function of the height of the vegetation which will be planted.
One other challenge when modeling a green rooftop is the management of the water and especially the evacuation of the over of water thought the drainage.
Parameters
Below are the three parameters to control my parametric model:
- The height of the vegetation
An intensive green rooftop is often build on a new building or a new infrastructure. It is directly integrated in the project (for the definition of requirements), that’s why I choose the height of the vegetation as start parameter instead of the loading capacity. The loading capacity could be adapted as a function of the result desired.
The height of the vegetation is influencing the thickness of the growing media and the thickness of the drainage layer. These three layers are the biggest and the heaviest and therefore have a great influence on the total weight of the green rooftop.
- The free vegetation spaces
Some space has to be without vegetation to realize the maintenance, to have space for the other infrastructures that may have to be on the roof (like mechanical ventilation equipment, solar panels…).
The free vegetation spaces are required by the norm NF DTU 43.1 for fire security and evacuation of the water.
- Other Parameters
The thickness of the protection layer and of the filter layer can be changed but these changes have a very few influences of the design challenge mentioned above.
Integration
The design of the green rooftop is directly linked to the design of the roof. For the combined parametric model, the shape of the green roof is designed with a plan, which is easier to integrate than a polygon.
Thus, the green rooftop is added to the supermarket and hospital roof, its shape is defined by the geometry of these two structures.
The green roof is added to the roof of the supermarket and to a part the hospital roof, with free place for the building equipment.
[1] http://www.diystart.com/
[2]Green roofs as a tool for solving the rainwater runoff problem in the urbanized 21st century? Jeroen Mentens, Dirk Raes, Martin Hermy, http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.473.599&rep=rep1&type=pdf
[3] http://dcgreenworks.org/