1. Introduction:
In the ontology assignment, we developed the ontology for Highway pavement with different components and design parameters. In this assignment, we modelled the system with these deign parameters through Dynamo BIM which gives us a better overview of how the parameters affect the system. The flexible pavements are designed for Expressway, National Highways, State Highways, Major District Roads, and other categories of roads.
2. Design challenge:
Flexible pavements are generally designed to fulfill two main requirements:
(i) to limit the elastic deformation of the pavement within the permissible limits so that the pavement can sustain a large number of repeated load applications without resulting in fatigue failure of the pavement layers.
(ii) to restrict the vertical strains on the subgrade and other pavement layers within desired limits so that the accumulated non-recoverable deformation in the form of rutting of the pavement surface along the wheel paths is within permissible limits during the design life of the pavement.
(iii) the third can be, to know the total cost of the construction project that is for excavation or embankment and procuring of materials according to the thickness and area of the pavement.
For fulfilling the above requirements, it is necessary to determine the proper thickness of various components of flexible components. There are different methods to design flexible pavement. We have used the IRC Method of Flexible Pavement design. Using the following simple input parameters, appropriate designs could be chosen for the given traffic and soil strength: CBR value of subgrade: The California bearing ratio (CBR) value of the subgrade soil. Design traffic in terms of cumulative number of standard axles (CSA) o Initial traffic: Estimated traffic after completion of road construction o Design life o Traffic Growth rate % o Vehicle Damage factor (VDF value) o Lane Distribution factor
3. Logic of the parametric model:
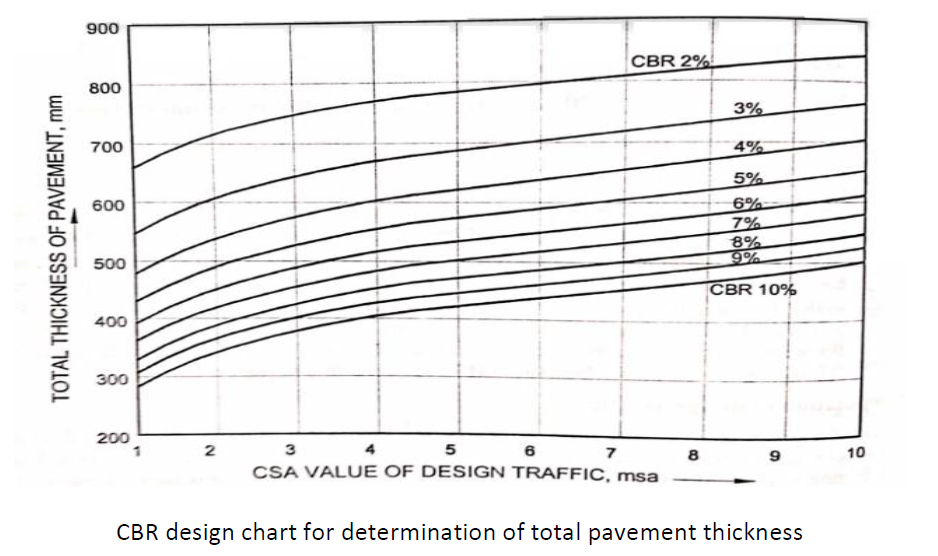
As discussed above, we must design the thickness of different components of the pavement. The total thickness of the pavement is decided based on the design factors such as CBR value of subgrade soil and design traffic. The combined effects of the factors are represented in terms of ‘Cumulative Standard Axles’ in terms of million standard axles (msa).
3.1. Mathematic relation
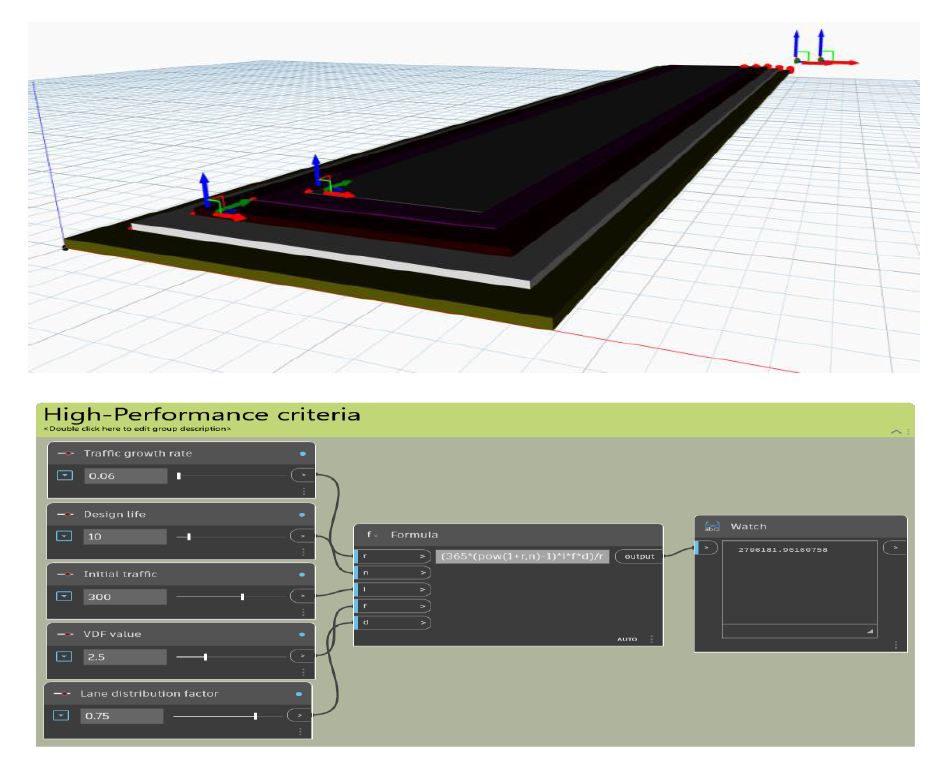
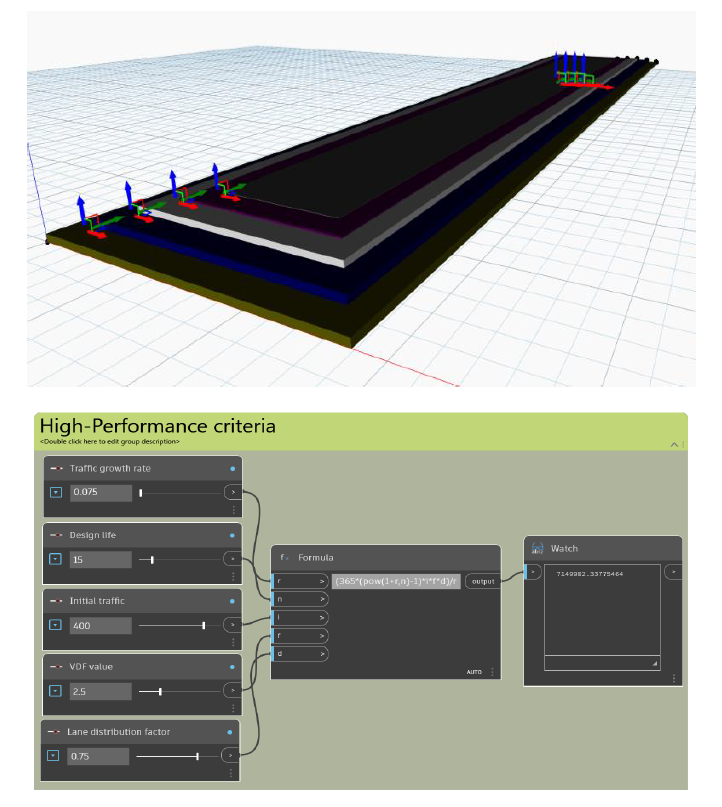
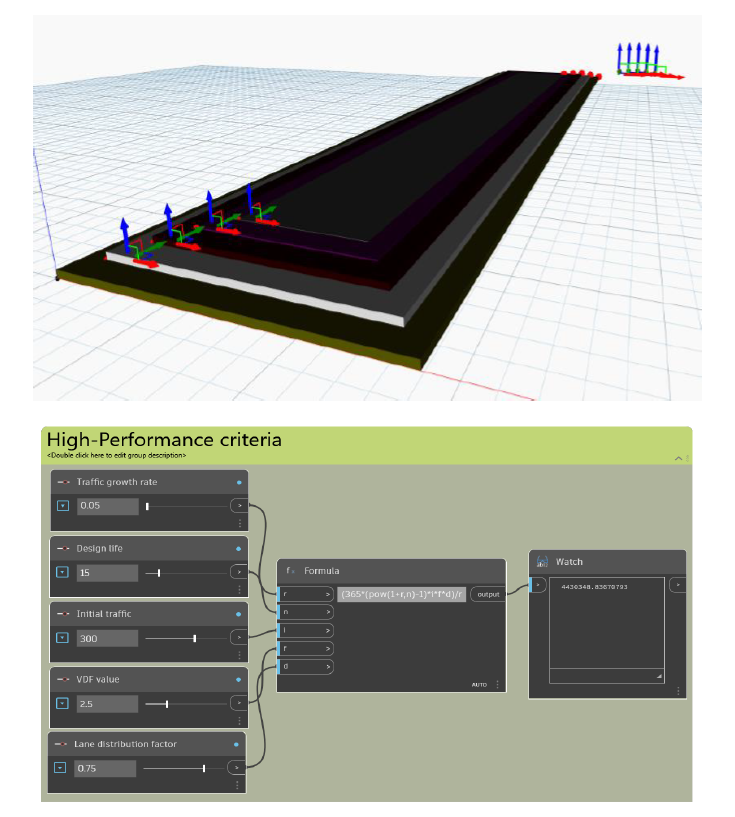
The design CSA value of vehicle category is given by; CSA = 365{(1+r)n-1}ifd/r where, r = Traffic growth rate n = Design life of pavement i = initial traffic on completion of road f = VDF value d = Lane distribution factor (0.75 for double lanes)
Then using the CSA value in terms of million standard axles (msa), we determine the total pavement thickness with the help of CBR design chart.
As per the IRC guidelines, the thickness of the component layers of pavement is decided.
4. Design space:
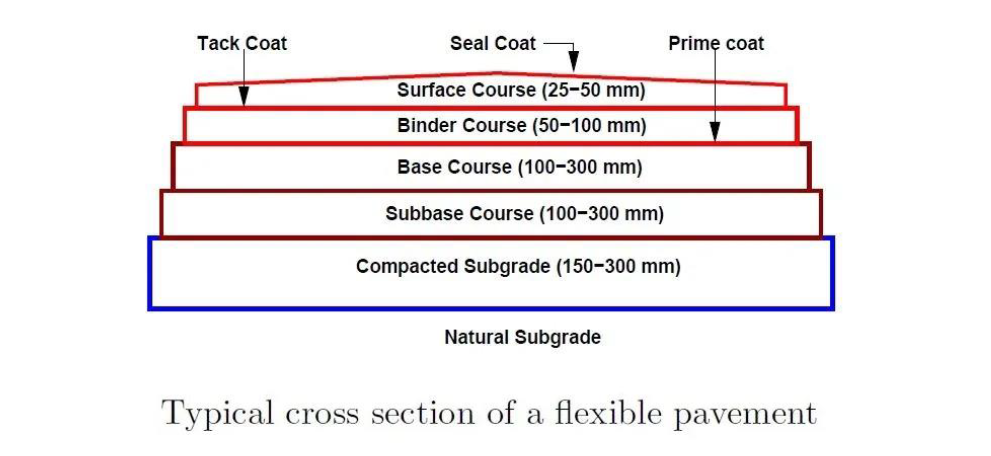
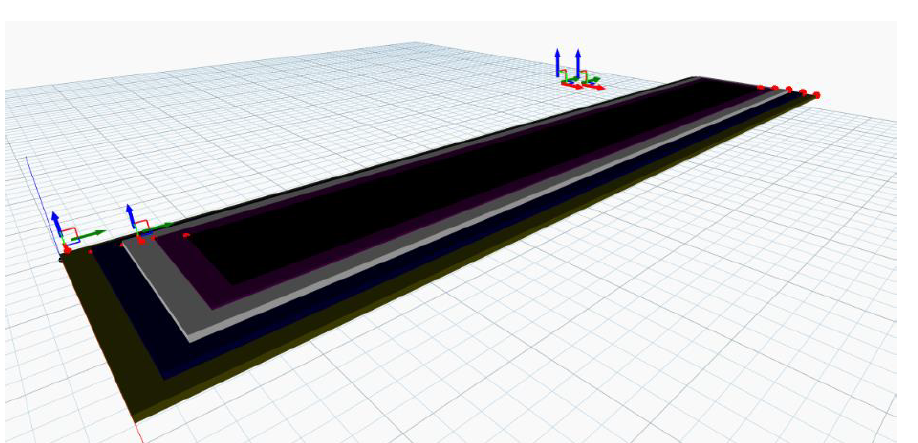
The model shows the overview of the flexible pavements consisting of the components of the typical flexible pavement. Different colors are attributed to the different components to easily differentiate between them. Green = Compacted Subgrade; Blue = Sub-base course; White = base course; Purple = Binder course; Grey = Surface course. In Dynamo BIM, the values of the thickness of components of pavement and the values of the design parameter can be easily changed. For the equation of the mathematical relation, we have used the ‘formula’ from library. So, putting the inputs will give the output to the equation through ‘watch’.
5. Design alternatives:
- Alternative 1 CBR value = 5%
- Alternative 2 CBR value = 4%
- Alternative 3 CBR value = 5%
We experimented with the model, by inputting different values to high performance criteria which gave us the different total thickness of the pavement and its components. We noticed that as the CSA value increases, the volume of the pavement increases. In second alternative, the CBR value is low, but the CSA value is high which leads to an increase in volume of pavement. Which means the amount of traffic on the pavement plays an important role in deciding the design of pavement. The model also helps in knowing the cost of construction.
Here you can Download the Parametric Model: highway-pavement
Here you can Download the Ontology: highwaypavementontology