Design Challenge
The design challenge for this parametric modelling assignment is to create a parametric model of a tiny house. The Tiny House is a compact dwelling that requires careful consideration of various parameters to achieve an optimal design. The design should balance factors such as weight, usable internal space, material volume, available roof area and usable floor area. The aim is to explore the design space and identify alternative solutions that meet specific performance criteria.
High Performance Criteria
Generating design alternatives with Dynamo and the selected parameters can lead to combinations of shapes and sizes that are not always practical in reality. Therefore, some High Performance Criteria (HPC) can help to evaluate the quality of the generated design. In Germany, there are clear specifications that a Tiny House on Wheels has to fulfil in order to obtain a road permit [1].
The five HPCs selected for this task are described below.
HPC: Weight of Tiny House
The weight of the Tiny House is an important consideration, affecting transport, foundation requirements and overall structural stability. For example, a Tiny House on wheels is not allowed to weigh more than 3500 kg, including the mobile base [1]. It is important to optimise the design to minimise weight while ensuring structural integrity.
HPC: Internal space volume of Tiny House
The interior space volume is a key factor in the comfort and functionality of the tiny house. It influences the layout of the room and the possibilities for use. A well-designed interior contributes to a more livable environment. For example, the available internal volume also determines the type and power of the heating system chosen.
HPC: Volume of Materials Required
Knowing the volume of material required is crucial for cost estimation and resource management. Minimising material consumption without compromising structural strength is an important aspect of sustainable design.
HPC: Available Roof Area
The available roof area is a critical parameter, especially in the context of different roof constructions. In the case of a flat roof, it could be used as a terrace, while other roof types can accommodate solar panels. This criterion is about the multifunctional use of the roof area.
HPC: Usable Floor Area
Usable floor space is a fundamental aspect of tiny house design. It has a direct impact on the functionality and comfort of the living space. For example, a Tiny House on wheels needs to be a maximum of 2.55 metres wide and 4 metres high to be approved for road use in Germany [1]. Non- mobile tiny houses have a maximum floor area of 50 m2 to be considered as such [2]. Optimising the use of floor space, considering design and legal restrictions, is essential for a successful tiny house design.
Design Parameters
Parametric Model Description
The parametric model is created with Dynamo BIM using the specified design parameters to generate the geometric configuration of the timber frame Tiny House. The Dynamo script is shown in Figure 2. The model can be divided into 3 big groups: (A) input parameters, (B) generation of main structure, (C) calculation of high-performance criteria.
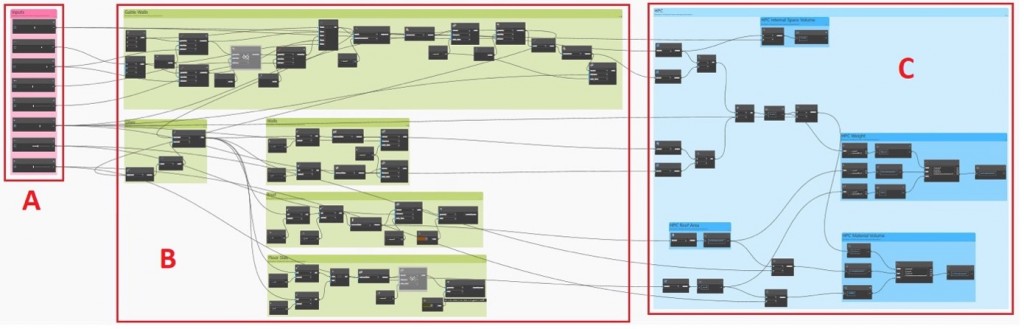
Group A includes the parameters shown in Table 1, which can be customised. In Group B, the geometric shapes for the floor slab, roof and walls have been generated. Finally, in Group C, all the performance criteria mentioned in Chapter 2 are calculated and returned as a result: the internal volume and weight of a timber frame tiny house, the available roof area, the usable floor area, and the volume of materials required.
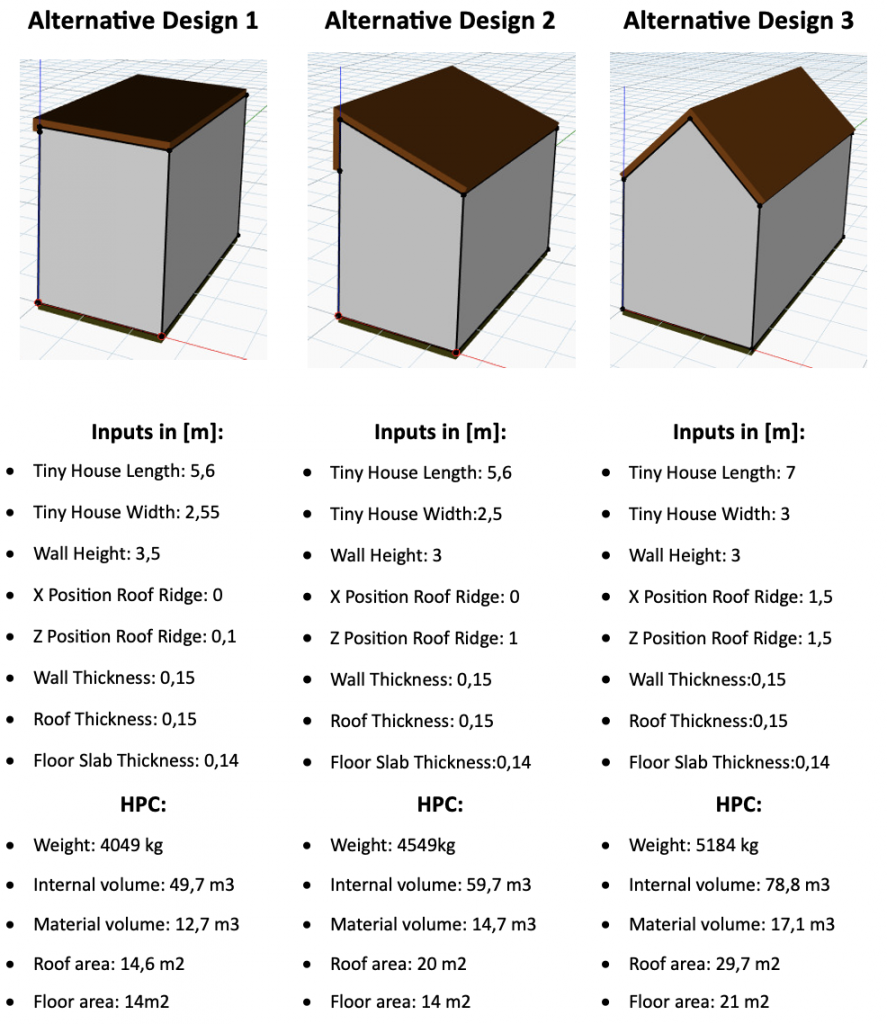
Design Alternatives
Three design alternatives are presented to showcase the flexibility of the parametric model:
While the parametric model provides valuable insights, it has limitations, such as the lack of consideration of certain cross-parameters, such as structural stability. These discrepancies can be addressed in more advanced versions of the model in subsequent project phases.
In conclusion, the parametric modelling of the timber frame tiny house provides a systematic approach to explore design alternatives based on specific performance criteria. The alternatives presented demonstrate the adaptability of the model to different design preferences and constraints.
Parametric Model
References
[1] „Tiny House Fakten – Die wichtigsten Informationen im Überblick“, Tiny House Tour, 17-Mai-2020. [Online]. Available at: https://tiny-house-tour.de/tiny-house-ein-neuer-trend/tiny-house-fakten-die- wichtigsten-informationen-zu-den-kleinen-haeusern/. [Accessed: 06-Jan-2024].
[2] Tiny House Verband e.V., “FAQ – Tiny House Verband,”, [Online]. Available at: https://www.tiny- house-verband.de/faq/ [Accessed: 29-Dez-2023]