Home / Group 2 / Integration Context of the Civil Systems
The systems considered for integration are Concrete gravity Dam, Tunnel, Water Pipe and Drainage Pipe system. The complete life cycle assessment of each system is given in their corresponding pages.
Major Systems
Concrete gravity dam – A gravity dam is a dam constructed from concrete or stone masonry and designed to hold back water by using only the weight of the material and its resistance against the foundation to oppose the horizontal pressure of water pushing against it. For the life cycle assessment a life cycle analysis on the stilling basin was carried out.
Tunnel – A tunnel is an underground passageway, dug through the surrounding soil/earth/rock and enclosed except for entrance and exit, commonly at each end. A pipeline is not a tunnel, though some recent tunnels have used immersed tube construction techniques rather than traditional tunnel boring methods.
Water Supply Pipe – A water pipe is any pipe or tube designed to transport drinking water to consumers. Materials commonly used to construct water pipes include cast iron, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), copper, steel or concrete. The aim of a distribution network is to supply a community with the appropriate quantity and quality of water. There are four network types: dead end, gridiron, circular and radial systems.
Drainage Pipe – Drainage means controlling of water during and after the construction of the any structural system. Controlling of water is attained by preventing excess quantity of water from entering the systems and removing the water that does enter.
Designing high performance engineering systems always face challenges at various facets of its evolution.
Major challenges faced during integration of our systems are:
- The integration of major systems with subsystems with lesser parametric interdependencies.
- Maintenance planning adopted since maintenance of subsystems vary from systems.
- Alignment of maintenance strategies.
- Influence of system interventions with subsystem interventions.
- Final multi-objective design optimization.
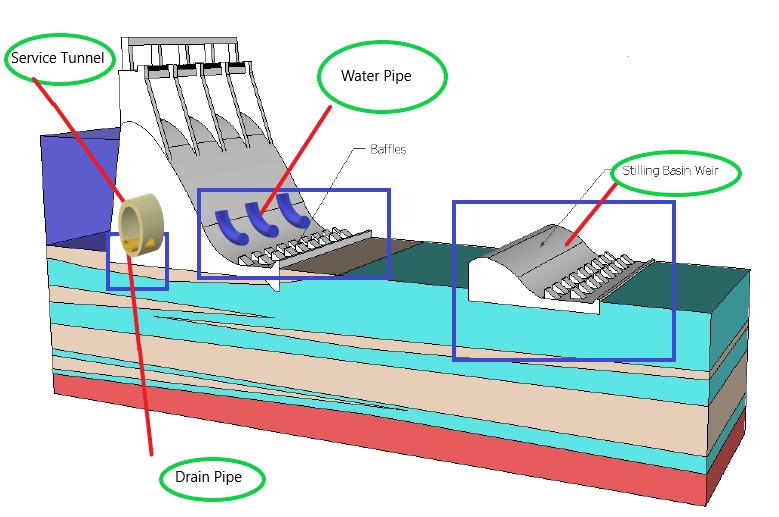
Therefore while considering the integration we have considered the Dam as an interface with stilling basin as a subsystem. In this study in order for integration we have assumed tunnel to be a service tunnel which facilitates the service of dam at frequent intervals. Again for integration of water pipe we had assumed it as aligned along the width of dam supply water from upstream to downstream. For integration of systems, drainage pipe is considered as running along the tunnel to drain the water seeps into dam and tunnel.
Final Integrated System – High-performance Dam