Introduction
A road is a constructed pathway for vehicular and pedestrian travel, typically made of asphalt, concrete, or gravel. Asphalt offers flexibility and durability, while concrete provides a rigid surface suitable for heavy traffic. Gravel roads, though cost-effective, may require more maintenance. Throughout their lifespan, roads endure dynamic traffic loads, weather fluctuations, and environmental exposure. Maintenance activities, including regular repairs and resurfacing, are crucial to counteract wear and tear. Additionally, the aging and degradation of road materials over time necessitate careful management. The overall resilience and longevity of roads depend on thoughtful design, construction practices, and proactive maintenance to withstand the diverse challenges posed by traffic, weather, and environmental factors.
Scope and goals
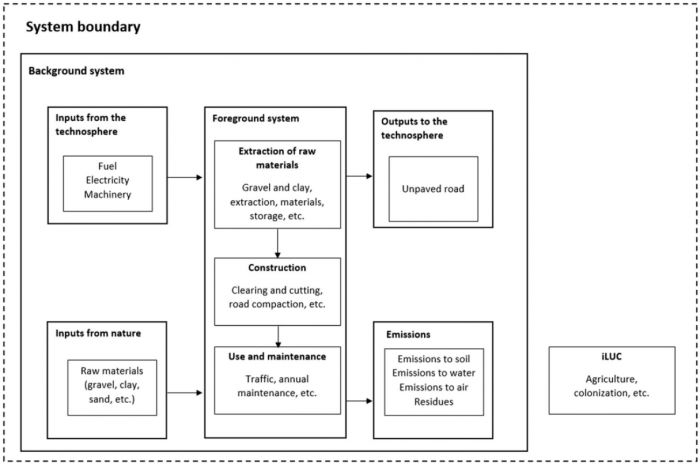
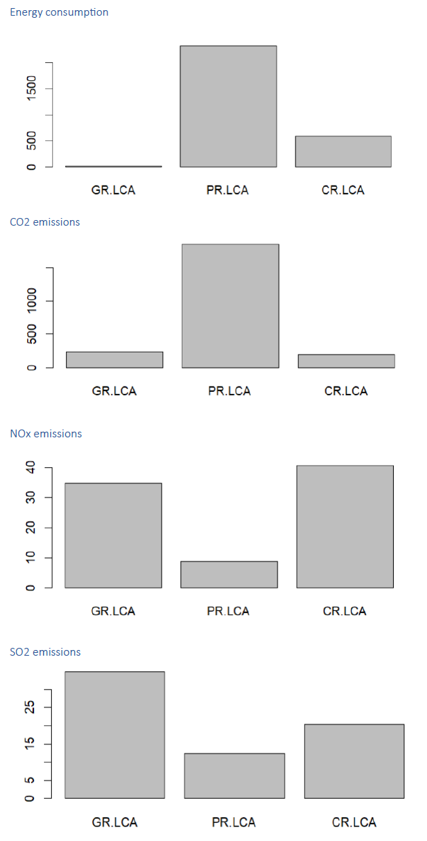
The main goal of this is to do a carbon footprint analysis. The scope and the boundaries of the assessment are presented in the figure below.
This includes the processing and production of raw materials for the road system, the production of inputs into construction and the maintenance of road service life, as well as energy consumption and emissions of CO2, NOx and SO2, which are major contributors to the global warming problem.
Design Options
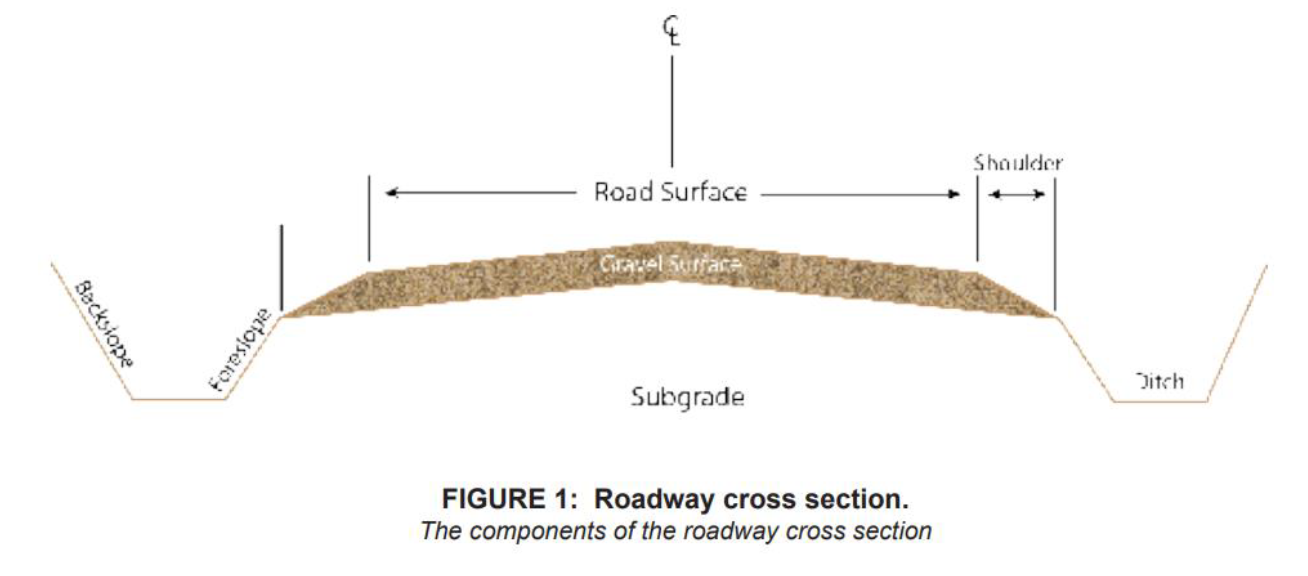
Gravel Road
A mix of stone, sand and fine-sized particles used as base on a road. Gravel may come from natural or quarry sources. Particle size distribution: 70% coarse, 30% fine.
Pavement Road
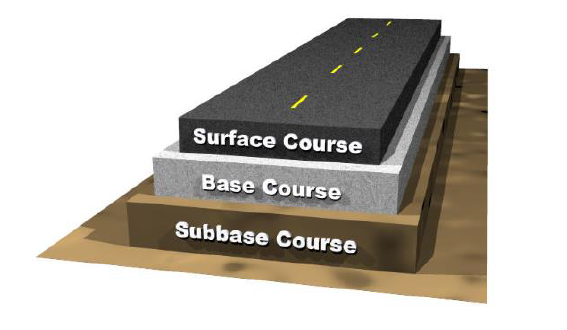
An asphalt pavement road is a flexible surface designed for vehicular and pedestrian use. It comprises layers such as subgrade, subbase, base course, and the top surface course made of asphalt. This layering system provides flexibility, durability, and resistance to cracking, ensuring a smooth driving surface. The subgrade supports the road structure, while the various layers work together to distribute loads effectively, enhancing the overall strength and performance of the pavement.
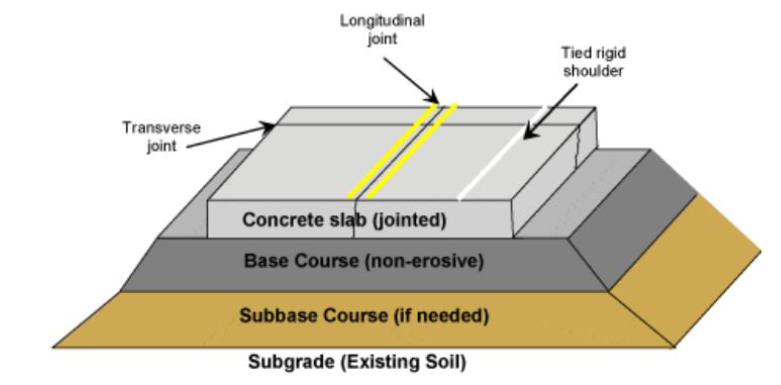
Concrete Road
Rigid pavement is a type of road construction using stiff materials like concrete. It provides durable and strong support for heavy traffic loads. Its rigid structure minimizes deformation and requires less maintenance compared to flexible pavements.
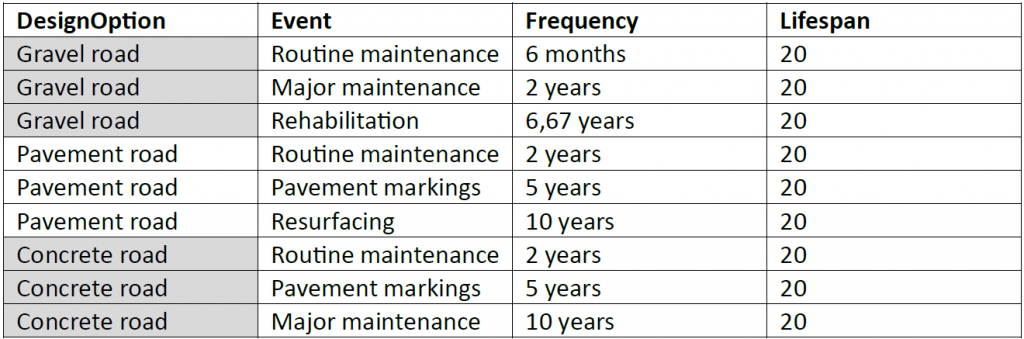
Life Cycle Timeline
Visualizing the life cycle of civil-engineered systems provides a clear representation of when specific interventions, such as repairs, replacements, and maintenance, are required. For this road example, there is a list of interventions with frequency of occurrence for each design option.
Life Cycle Inventory and Analysis
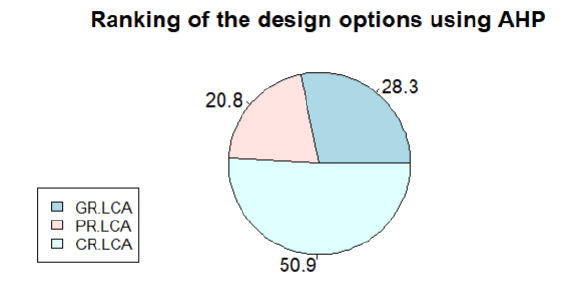
MDCM – Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP)
The decision problem is broken down into a hierarchy. At the top level, you have the goal, followed by criteria that affect the decision, and finally, the alternatives.