Component: Conduit pipe
The selected component of the dam is the pipe used to create a conduit. Conduits convey water away from the reservoir for different purposes. The defining parameter of the pipe is the inside (Di) and length (Li). The chosen design of the component is a corrugated HDPE (High-density polyethylene) pipe, a sketch is provided in figure 1. The following assessment of the maintenance strategies for the pipe is based on the technical manuals for conduits and pipes of the Federal Emergency Management Agency (2005, 2007), an agency of the United States Department of Homeland Security.
An HDPE pipe is made with resins, that consist of polymerized molecules mixed with fillers, lubricants, stabilizers, and sometimes pigments. The service life is approximately 50 to 100 years, depending on the pipe’s structure, the water and soil chemistry and water flow. The chosen pipe is double walled with a corrugated outer shell and a solid inner lining. While an HDPE pipe requires little maintenance, it is recommended, that the pipe is flushed every 8 to 12 years (CF.dam). Most HDPE pipes are encased in concrete to assure quality compaction against the conduit. Movement in the conduit space can cause cracks, which must be grouted over (GR.dam) every 18-22 years. The pipe should also be sliplined (SL.dam) every 20-30 years, which means a smaller, one walled pipe is inserted into the existing pipe. All these measures can extend the service life of an HDPE pipe greatly.
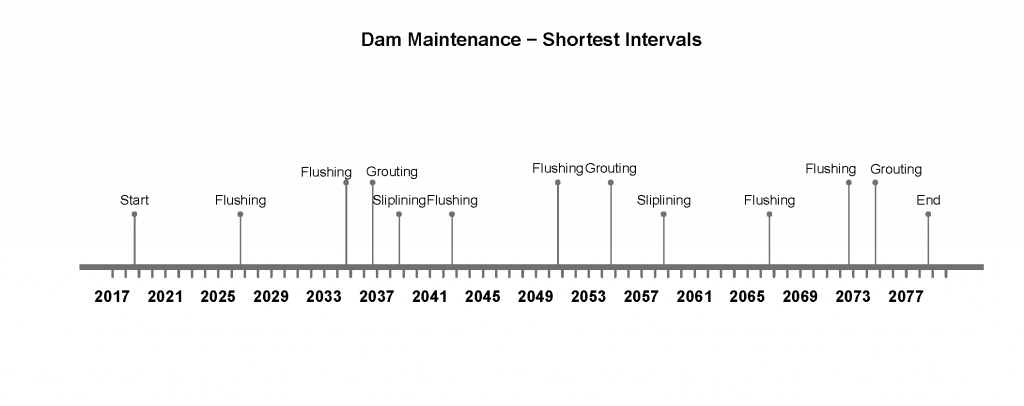
Figure 2 represents the timeline in case the maintenance is done as often as possible, which means the lowest value of the maintenance interval range is chosen. This would be the case if the system is bigger and therefore must withstand higher loads. Another reason could be increased earth movement, for example, if the dam is built in a seismically active area. The water and soil chemistry also can require a more frequent maintenance of the conduit.
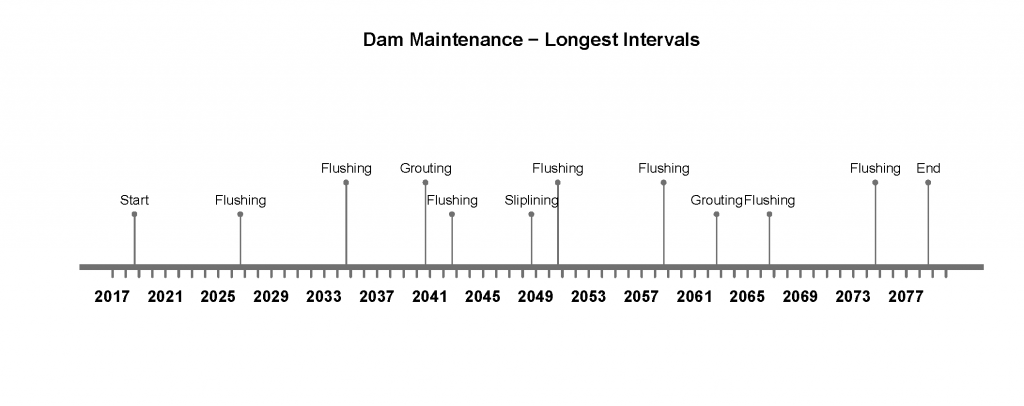
Figure 3 represents the opposite timeline, where the maintenance is done at the highest value of the maintenance interval range. This would be the case for smaller dams and favorable conditions.
Sources:
Federal Emergency Management Agency, 2005. Technical Manual: Conduits through Embankment Dams. https://www.fema.gov/media-library-data/20130726-1515-20490-8766/fema484.pdf
Federal Emergency Management Agency, 2007. Technical Manual: Plastic Pipe Used in Embankment Dams. https://www.fema.gov/media-library-data/20130726-1633-20490-0008/femap_675part1.pdf
ADS, 2015, N-12 Brochure, https://www.ads-pipe.com/sites/default/files/Brochure_N-12_(09-15).pdf

