Design Challenge
The primary challenge in residential building design is to balance energy efficiency and construction costs while maintaining functional and aesthetic quality. By using parametric modeling, designers can systematically explore various configurations to achieve optimal performance.
High-Performance Criteria
Two high-performance criteria are considered for evaluating the parametric designs:
- Energy Efficiency – Measured using the Surface Area-to-Volume Ratio (SA/V) and Energy Use Intensity (EUI).
- Construction Cost – Estimated based on material usage, including concrete and steel volumes.
Design Parameters
The following input parameters are used to define the residential building’s geometry:
| Parameter | Min. Value | Max. Value | Step Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Height (H) | 5m | 15m | 1m |
| Floor Height (fh) | 2.5m | 4m | 0.5m |
| Length (L) | 6m | 25m | 2m |
| Width (W) | 6m | 25m | 2m |
Material specifications:
- Concrete structure with steel reinforcement
- Wall thickness: 0.3m
- Floor slab thickness: 0.2m
Parametric Model Description
The model is built using Dynamo BIM, where each parameter dynamically influences the building’s geometry and material consumption.
- Building Height (H): Defined based on floor count and floor height.
- Building Footprint (L × W): Controls horizontal dimensions, impacting energy and material use.
- Material Volume Calculations: Determines required concrete and steel for cost estimation.
Design Alternatives
Three design alternatives are developed:
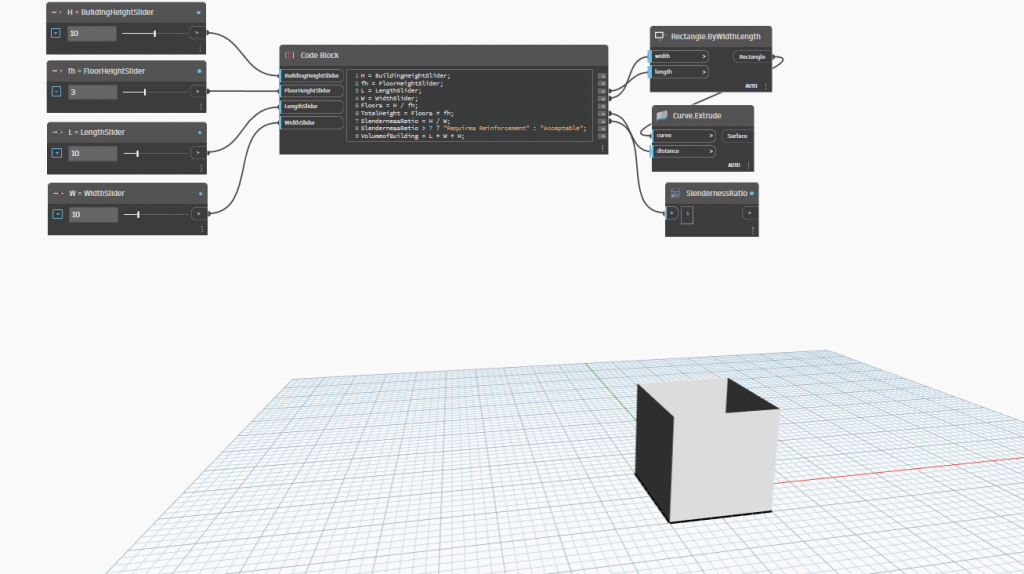
Model 1: Base Case
- Parameters: H=10m, fh=3m, L=10m, W=10m
- SA/V Ratio: 0.6
- Energy Consumption: 15,000 kWh/year
- Total Construction Cost: 22,750 USD
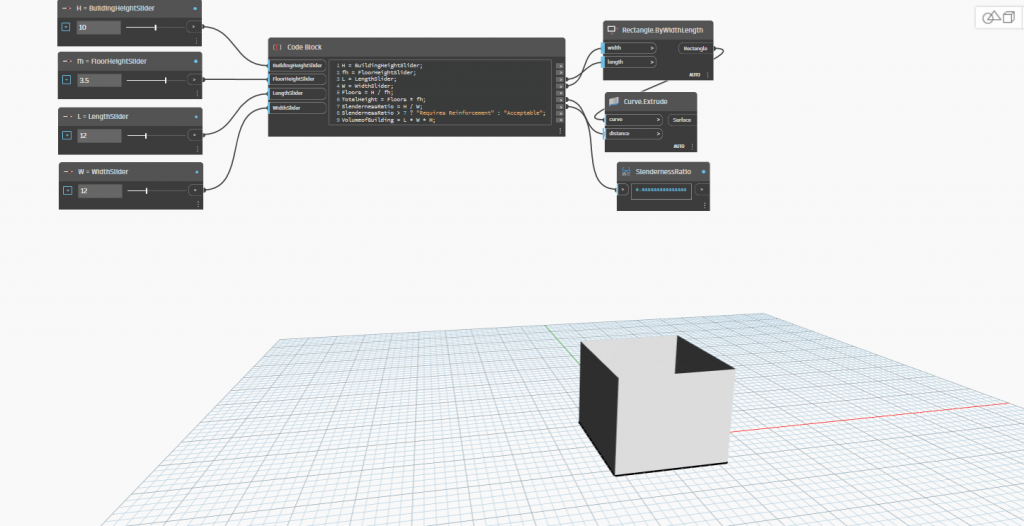
Model 2: Energy-Optimized Design
- Parameters: H=10m, fh=3.5m, L=12m, W=12m
- SA/V Ratio: 0.45
- Energy Consumption: 12,000 kWh/year (20% reduction from Base Case)
- Total Construction Cost: 25,025 USD
Model 3: Cost-Effective Design
- Parameters: H=12m, fh=3m, L=8m, W=8m
- SA/V Ratio: 0.7
- Energy Consumption: 11,520 kWh/year
- Total Construction Cost: 19,875 USD
Conclusion
The three models provide distinct advantages:
- Model 1 serves as a balanced reference.
- Model 2 prioritizes energy efficiency at a slightly higher cost.
- Model 3 minimizes construction cost but slightly compromises energy efficiency. Parametric modeling effectively enables performance trade-off analysis, assisting in informed decision-making for residential building design.