Scope and Goal
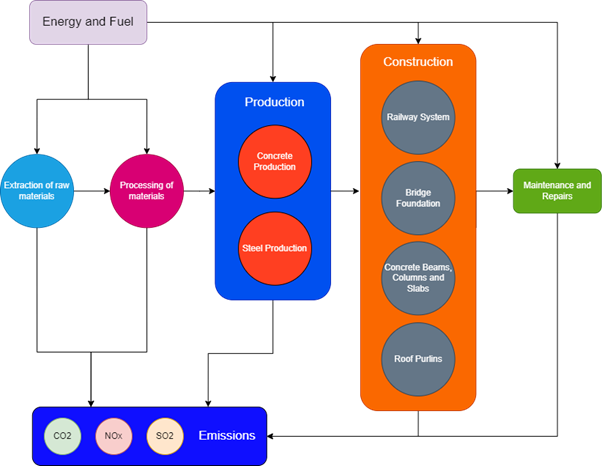
The purpose of this part is to assess the impact of the components throughout their life cycle on the environment. The process starts with the extraction of raw materials and then they are processed for production of required materials which would be used in construction of the specific components and finally the maintenance and repair cycles of the components. The scope of our assessment includes a concrete building structure with steel roof purlins, railway system and bridge foundation.
In this assessment, the energy and fuel required to produce the materials for construction and the energy and fuel required to for maintenance and repair of the components throughout their life has been considered. The scope and boundary of the system can be seen in Fig.1 below.
Figure 1: LCA Boundary and Goal
Life Cycle Inventory
A vital part of a Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is a Life Cycle Inventory (LCI), which entails compiling information on the system’s inputs and outputs over the course of its whole life cycle. A product or system’s life cycle impact (LCI) gives a thorough picture of the resources it uses and the emissions it produces. It also serves as the foundation for later life cycle assessments. This information can be used to pinpoint areas that need improvement in order to lessen a system’s negative environmental effects.
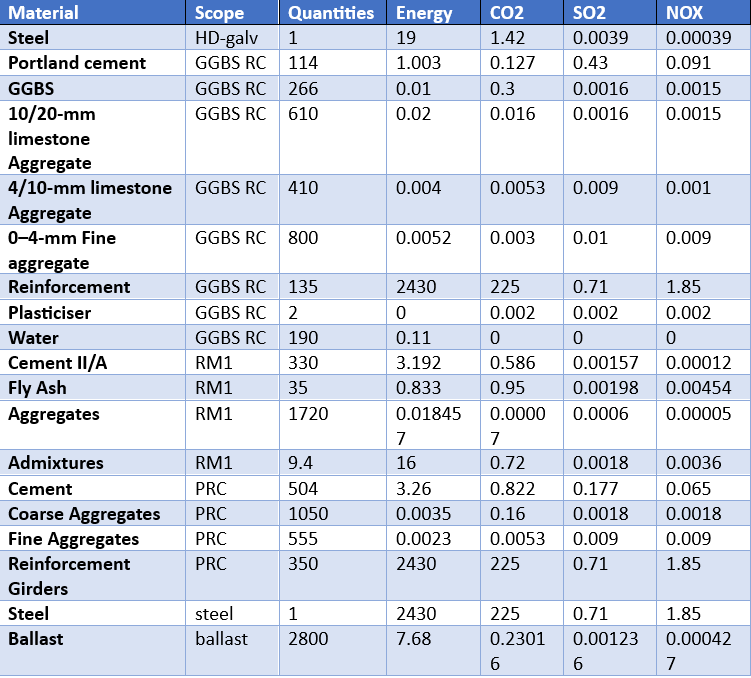
Table 1 below shows the LCI material file entailing quantities, energy consumption and emissions for the materials of the best design option in each system.
Table 1: LCI Materials Inventory
This file basically shows the quantities of materials required for each scope and the number of emissions. The units for these are Kg/m3.
Life Cycle Analysis
For this assessment, we took the best option from all subsystems. So, we ended up with 5 options from the subsystems which we used for the LCA.
| System | Component | Best design Option |
| Steel-structured factory | Roof purlins | Hot-dip galvanized steel |
| Private concrete villa | Slab | GGBS-RC |
| Frame structured building | Beam | GGBS-RC |
| Pile foundation | concrete pile | Ready mix 1 |
| Rail way system | Train rail | PRC + steel + ballast |
The life cycle analysis takes into account the maintenance interventions of all the individual subsystems. LCA provides the impact of the integrated system on the environment and also shows the number of emissions and the cost of the impact on the environment. The results of the LCA can be seen below:
Fig.2 results of the LCA
This shows that CO2 makes up the majority of the emissions almost around 98% of the total which is followed by Energy consumption, NOx and SO2 in that order respectively. According to the huge number of emissions it is evident that the cost of the impact on the environment would be a little high which can be seen in the figure above.