Timber Room Module – Window
Introduction
For modern student housing, the integration of sustainable and durable building materials is paramount. This individual project focuses on timber room modules as a promising solution, examining the critical component of windows and their frame materials alongside glaze options. By delving into various combinations of frame materials and glazing, this study aims to evaluate their respective impacts on window maintenance plans and conduct a comprehensive life cycle analysis.
Scope and goals
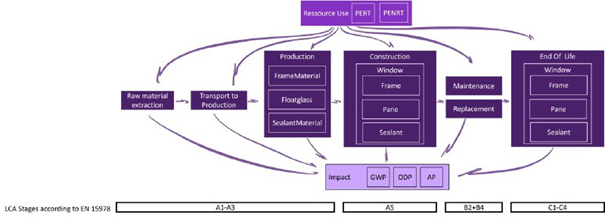
The goal of this life cycle analysis (LCA) is to calculate energy used (renewable and non-renewable), as well as the global warming potential (GWP), the ozone depletion potential (ODP) as well as the acidification potential (AP) resulting in the production as well as maintenance and replacement until the end of life of the windows in a modular timber room (Gradle to Crave).
The exact scope of the LCA will cover the extraction of raw materials, the transport to factory, as well as component production, construction, maintenance and end of life of the window components.
Design Options
Opt1: Vinyl Frame, Tripple Glaze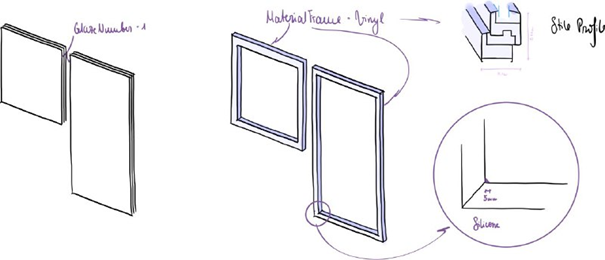
PaneMaterial = 0.034m3 (Floatglass) = 85.61kg
FrameMaterial = 0.072m3 (Vinyl) = 98.9kg
FrameSealant = 8.7e-5 m3 (Silicone) = 0.11kg
Opt2: Aluminium Frame, Double Glaze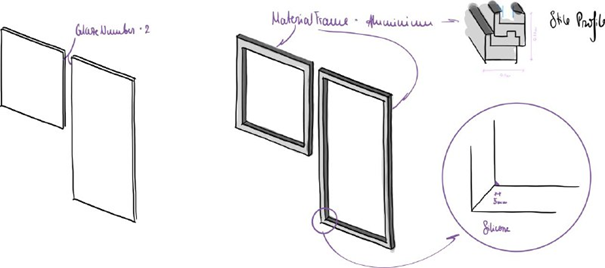
PaneMaterial = 0.023m3 (Floatglass) = 57.08kg
FrameMaterial = 0.065m3 (Aluminium) = 175 kg
FrameSealant = 8.7e-5 m3 (Silicone) = 0.11kg
Opt3: Wood Frame, Single Glaze
PaneMaterial = 0.011m3 (Floatglass) = 28.54kg
FrameMaterial = 0.143m3 (Wood) = 70.7kg
FrameSealant = 1.7e-4 m3 (Putty) = 0.21kg
Life Cycle Timeline
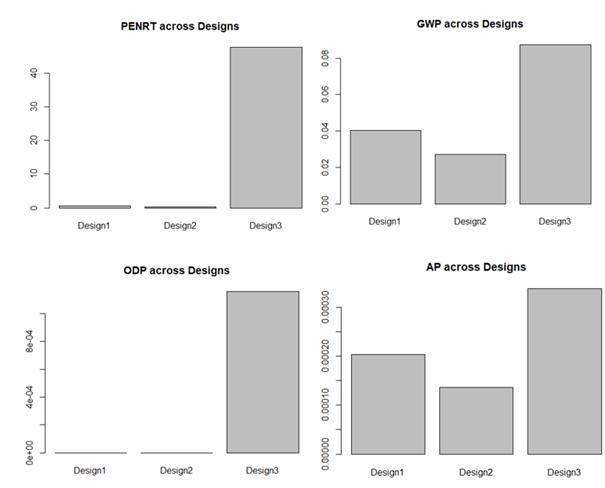
What we can see is that the third design has the highest resource use as well as impact on the environment, due to the larger mass of a solid wood frame compared to the hollow vinyl and aluminium frames.
The GWP as well as the AP are not as strong of a difference as in the PENRT and the ODP, because the substantial material (wood) has a low GWP and AP compared to vinyl and aluminium, however in total the mass still leads to the highest impact.
Between the first and second design, the second one seems to be less impactful because of the fewer material in the pane, as well as the fact that aluminium has a larger impact and uses more resources than vinyl in production.
Multi Criteria Decision Making
Now we see Design 1 favored by almost 50%, followed by Design 3 and Design 2 coming in last, which is a different result than we concluded previously.
When looking at only the absolute values of the LCA we only saw which one had the most or least resource use or environmental impact, whereas now we are weighting how much more or less which result is compared to the others.