Maintenance actions typically classified as preventative and substantial. Preventative maintenance actions taken to prevent deterioration and keep the structure fully operational while substantial maintenance actions are taken to repair an existing damage and improve the condition. Substantial maintenance work is usually comprehensive while preventative maintenance work is relatively small scale.
Preventative maintenance activities on bridges, roadways and tunnels are typically focused to reduce the impact of water and traffic. The main goals are as follows:
- Ensuring proper drainage of water
- Sealing the materials of structural elements from exposure to water
- Improving the surface conditions to prevent accelerated deterioration
- Providing proper guidance for drivers on the roadway, over the bridge and in the tunnel
Substantial maintenance activities on bridges, roadways and tunnels, on the other hand, are as follows:
- Extensive repair actions
- Replacements
INDIVIDUAL MAINTENANCE PLANS OF SUBSYSTEMS
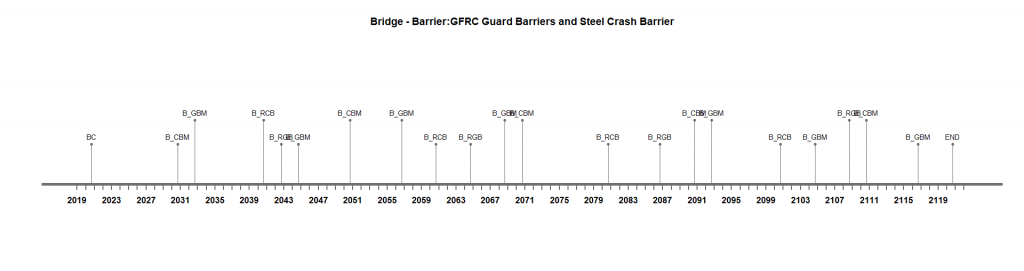
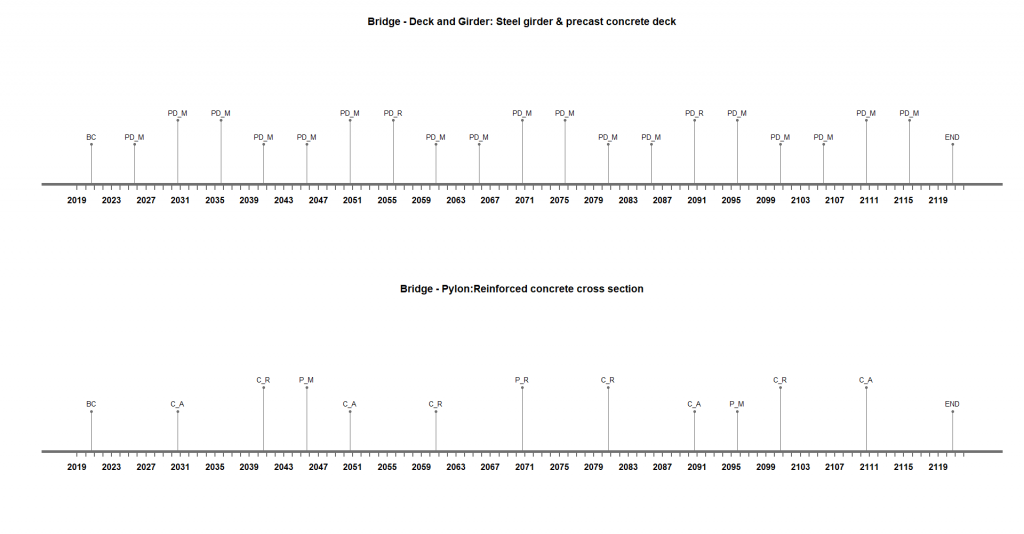
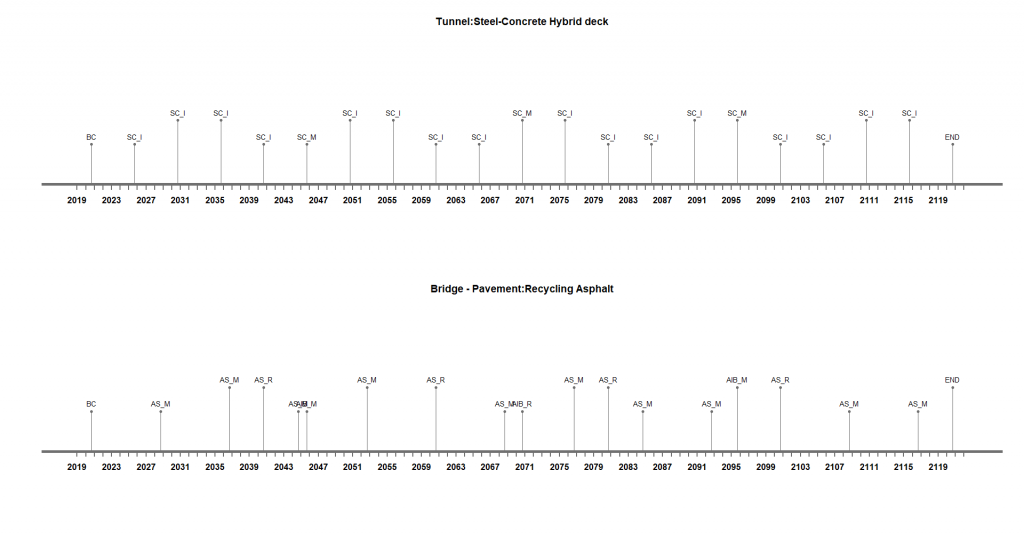
An efficient intervention plan for each component is required to obtain an efficient integrated system plan. Individual plans are shown below:
Fig 1. Individual timelines of Subsystems
| Type of Intervention | Abbreviation | Duration(days) | Ideal Frequency(years) |
| Precast Deck Maintenance | PD-M | 12 | 5 |
| Precast Deck Replacement | PD-R | 60 | 35 |
| Pylon Minor Repair (Surface) | P-M | 8 | 25 |
| Pylon Structural Repair | P-R | 40 | 50 |
| Cable Addition -> Inserting another wire into the tube | C-A | 2 | 10 |
| Cable Replacement | C-R | 10 | 20 |
| Maintenance of Steel Concrete Slabs | SC-M | 20 | 25 |
| External Inspection of Steel Concrete Slabs | SC-I | 5 | 5 |
| Asphalt Surface Replacement | AS-R | 7 | 20 |
| Asphalt Intermediate and Base Layer Replacement | AIB-R | 14 | 50 |
| Asphalt Surface Maintenance | AS-M | 2 | 8 |
| Asphalt Intermediate and Base Layer Mainenance | AIB-M | 2 | 25 |
| Crash Barrier repair and Minor maintenance | B-CBM | 1 | 10 |
| Replacement of Crash Barrier | B-RCB | 2 | 20 |
| Guard Barrier repair and Minor maintenance | B-GBM | 2 | 12 |
| Replacement of Guard Barrier | B-RGB | 7 | 22 |
Table 1. Interventions
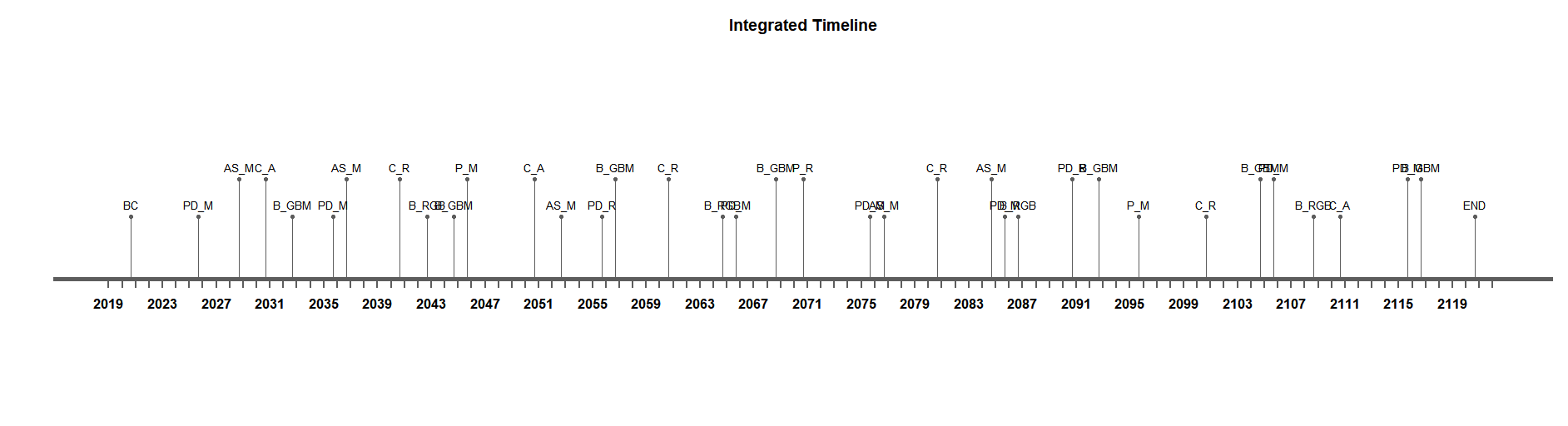
INTEGRATED STRATEGY
Maintenance of a civil system rely on information collected on its components, which can provide the us an accurate assessment of the overall condition state.
Our aim is to minimize the duration of the interventions and to maximize the gap between them. We can attain this goal by aligning the maintenance strategies of the subsystems. After integrating the maintenance plans of all subsystems, the following timeline and pareto plots are obtained:
Fig 3. Integrated Timeline
The optimal option would be obtained by is minimizing the duration of the interruptions and maximizing the distance between interventions. We can rank the alternatives to evaluate and select the best alternative which is the best for our preference.
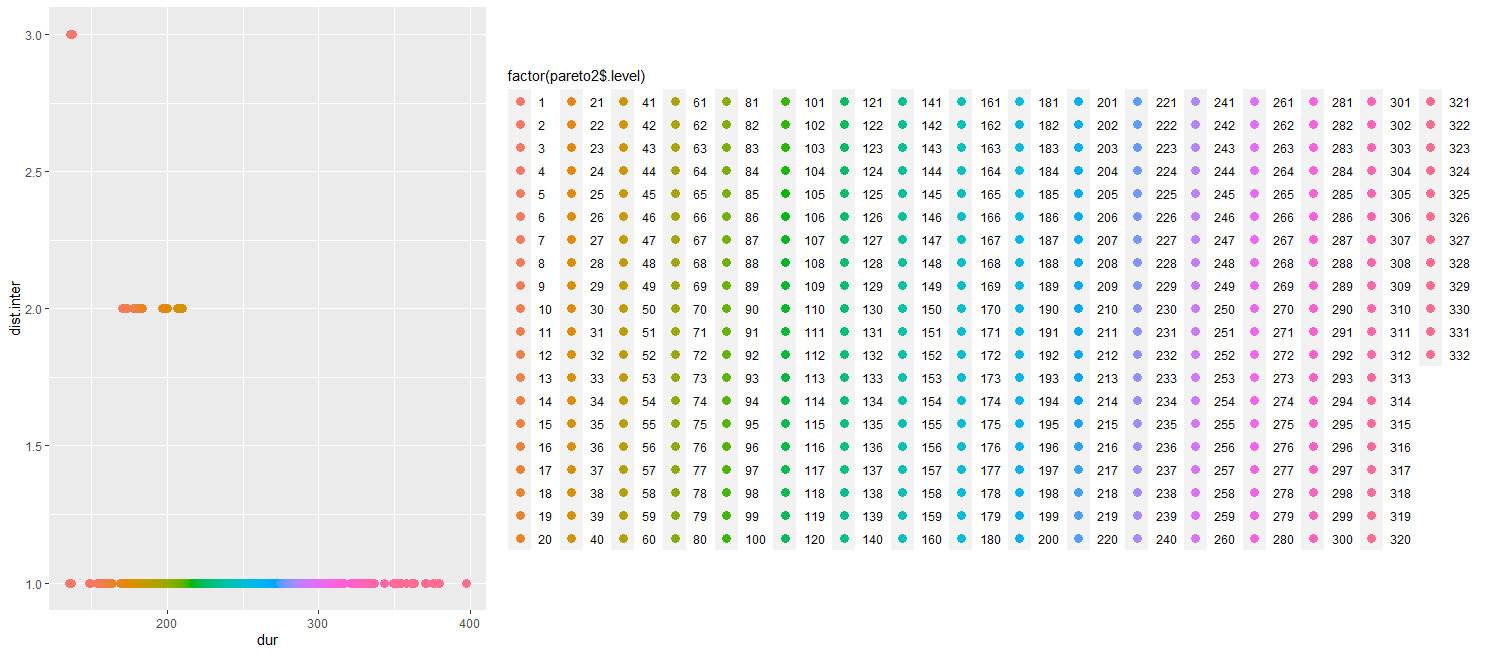
332 alternatives are ranked in the plot below based on our preference.
Fig 4. Ranking of Alternatives
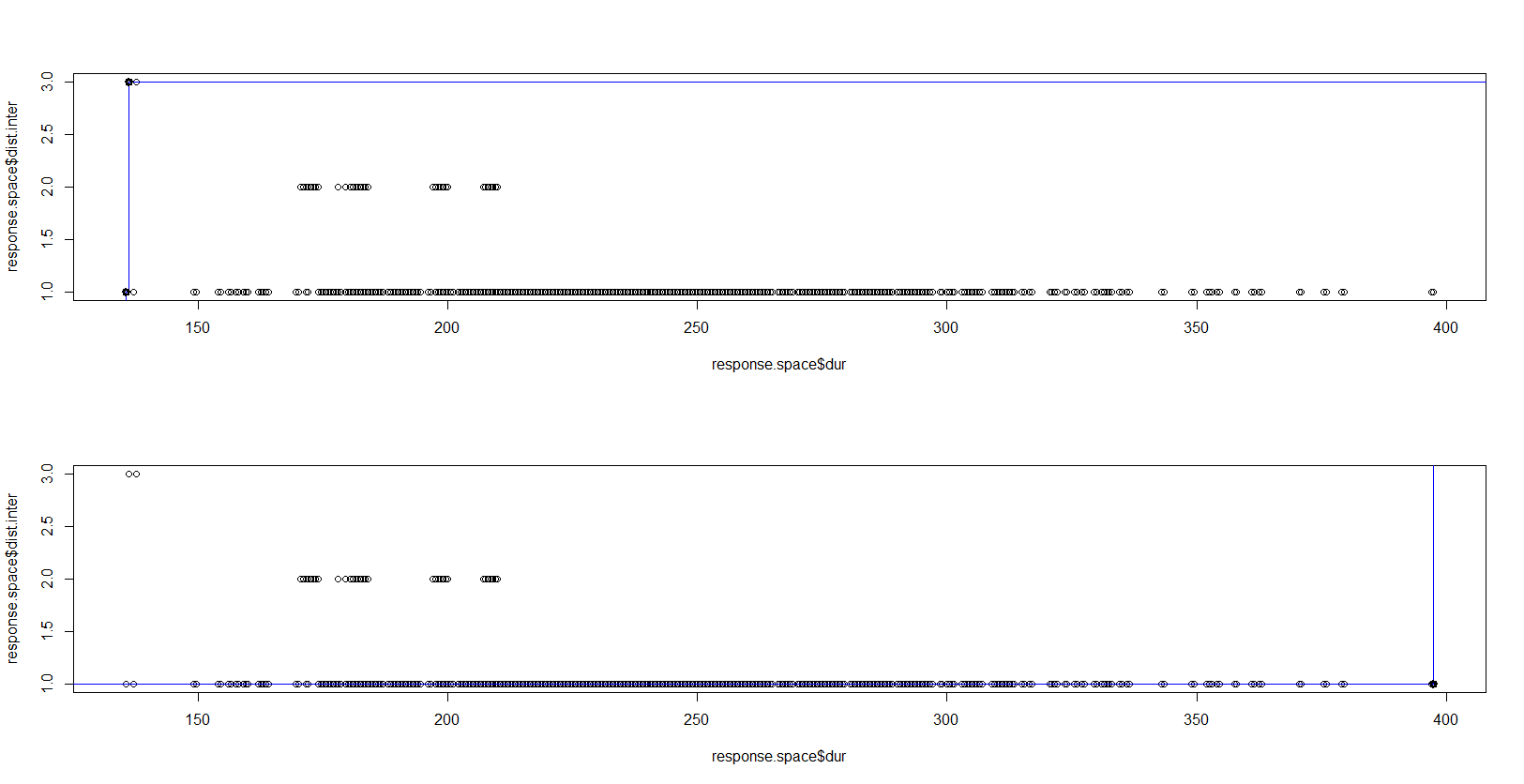
Our preference is visualized by the Pareto frontier in the first graph below. The blue line represents the Pareto frontier and the dark black point in the top-left corner represents the best alternative based on the preferences. In the second graph, the opposite case is represented, which is low distance and high duration.
Fig 5. Lowest Duration – Highest Distance and Highest Duration – Lowest Distance Alternatives
Go to next page: Life Cycle Analysis