“Sustainable Building Water Management”
In the pursuit of sustainable urban living, our integration context revolves around harmonizing water management, energy efficiency, and social considerations within multi-story buildings. This holistic approach combines cutting-edge technologies, thoughtful design, and comprehensive modeling to create an intelligent ecosystem.
Integration Challenges:
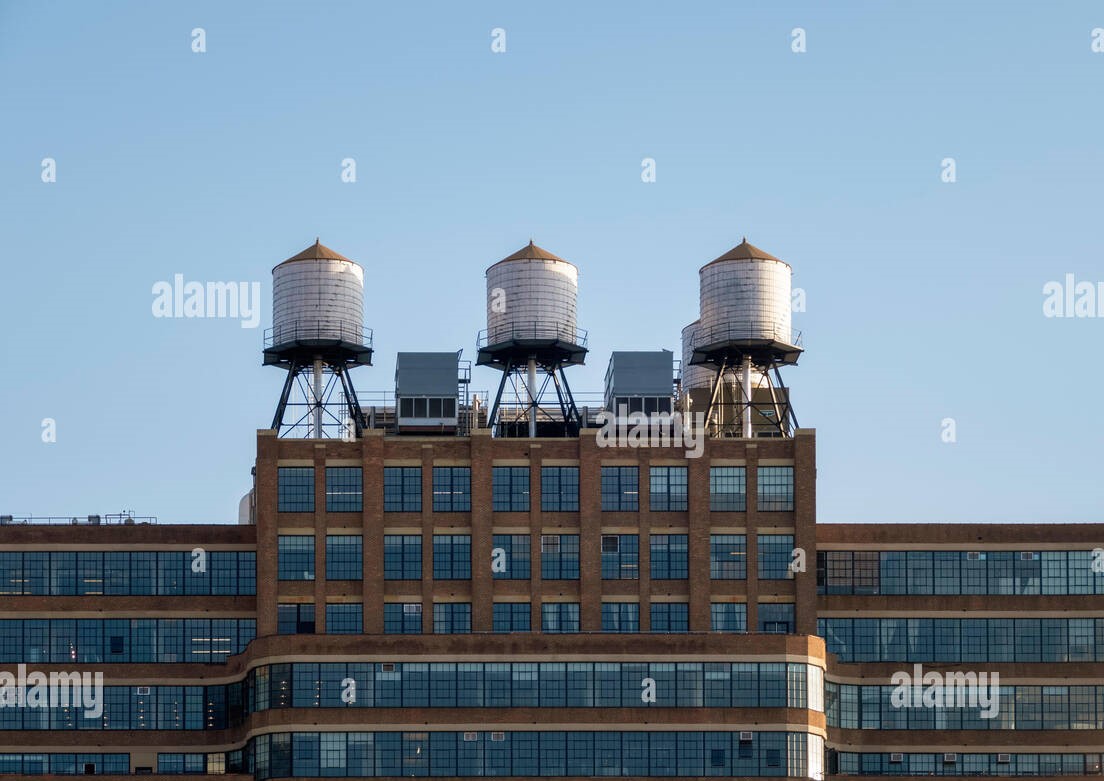
1. Elevated Water Tank and Total Shading Device:
- Installation of water tanks atop buildings to generate pressure and facilitate the supply of water to the households.
- Integration of shading devices on top for extensive energy-efficient building practices.
Image Source: https://www.alamy.com/typical-water-tanks-on-the-roof-of-a-building-in-new-york-usa-new-york-state-new-york-city-image255393162.html
2. Water Consumption Analysis:
- Determining the water needs based on the anticipated number of inhabitants.
- Optimization to minimize water wastage and promote sustainable usage.
Image Source: https://www.buildersmart.in/blogs/ways-to-reduce-water-usage-in-buildings/
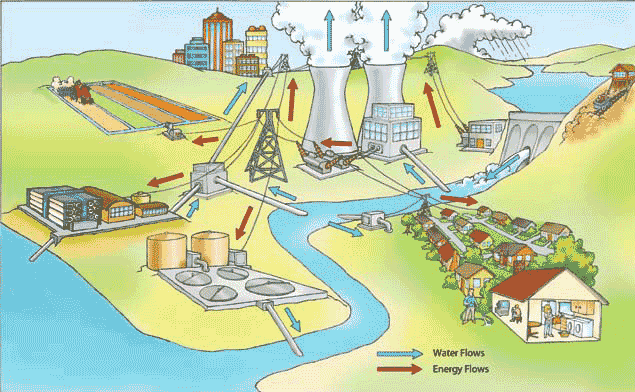
3. Energy Consumption Assessment:
- Monitoring and analyzing the energy consumption related to water systems.
- Identifying opportunities for energy efficiency and reducing environmental impact.
Image Source: https://19january2017snapshot.epa.gov/climate-impacts/climate-impacts-energy_.html
4. Dead Load Evaluation:
- Analysis of dead loads associated with water tanks on the building structure.
- Assessment of dead loads on the ground to ensure structural integrity.
5. River Proximity Analysis:
- Study of water flow dynamics near buildings located next to rivers.
- Evaluation of potential threats to the ground if river water levels rise.
6. Limitations Assessment:
- Identification and understanding of limitations inherent in the system.
- Consideration of constraints that may affect the effectiveness of water management strategies.
Image Source: https://www.csrmandate.org/importance-of-water-management-in-urban-environments/
Integration Framework:
Our integration framework relies on advanced ontologies and parametric models that facilitate real-time data exchange and adaptive decision-making. This interconnected system ensures a dynamic response to changing conditions, promoting sustainability and resilience.
Benefits and Goals:
- Efficient water management to meet building and community needs.
- Reduction of energy consumption through intelligent system integration.
- Socially responsible practices for community well-being.
- Enhanced structural safety through dead load analysis.
- Proactive measures to address potential threats from rising river levels.