Civil Engineering System: Heating System
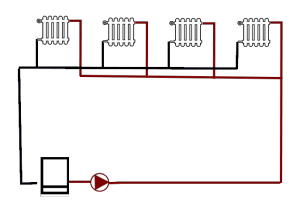
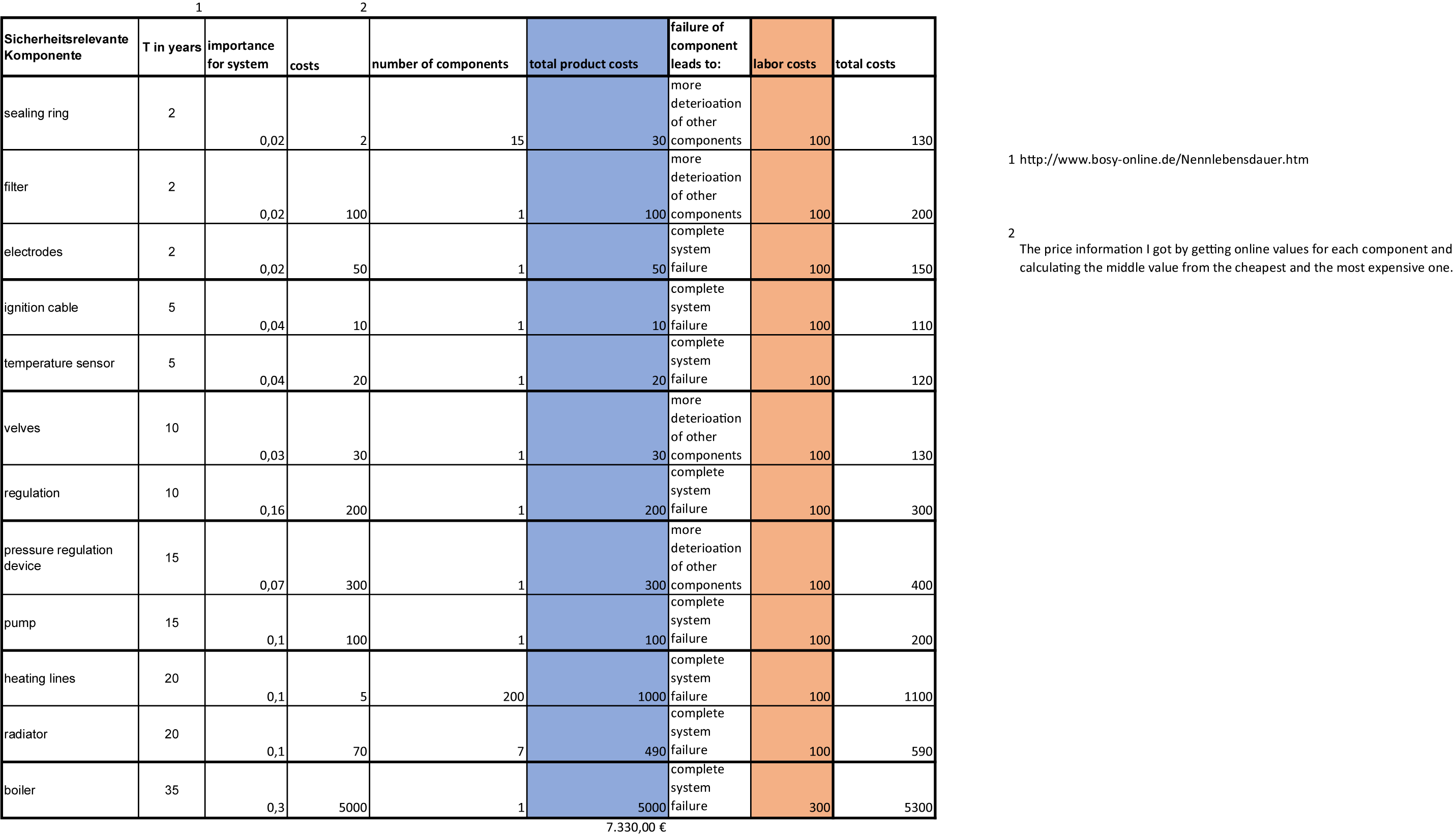
A heating system consists of heat generation and heat distribution. All relevant components and their lifetime and theier exchanging costs are presented in the table below. The heat is produced by the boiler. The heating circuit is a closed system. The return water is heated to the flow temperature and distributed in the radiators. To distribute the water a certain pressure is necessary. This is built by the pump. An expansion tank prevents pressure fluctuations. Through the pipes, the supply water is pumped to the radiators. These are flowed through with a certain flow of water and thereby heat the room. Between the individual components valves are installed, which limit the flow. This protects them from damage to the components. In the case of the flow regulators on the radiators, they ensure that the heating of the different rooms can take place uniformly. On connecting parts seals are installed, which protect against water and thus pressure loss in the system. In modern systems, there are also sensors and controls that can measure and control pressure, flow, and temperature.
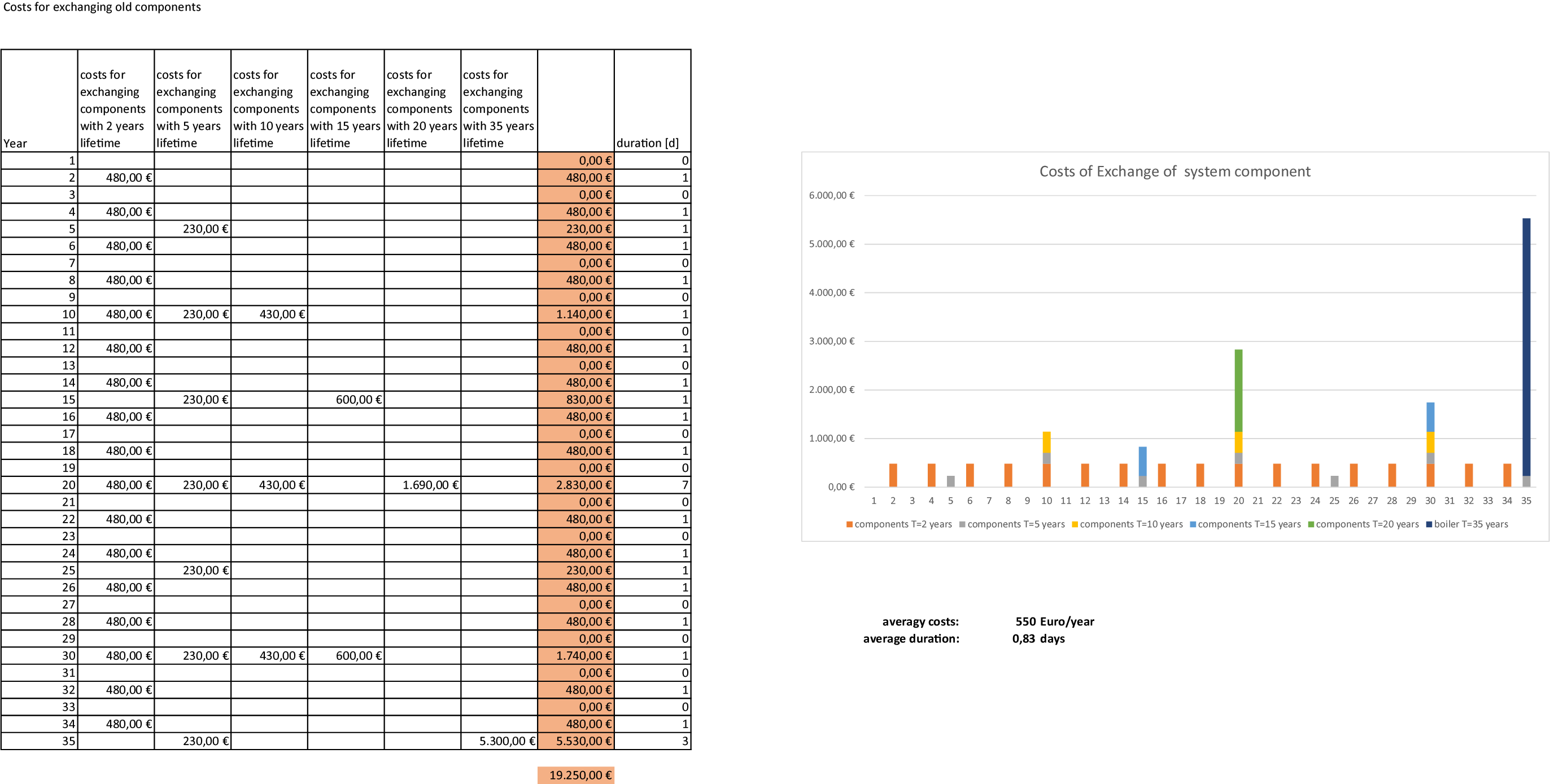
In the table the system need of exchanging components is presents. All components have to be exchanged when they reach their lifetime. Pump, pipes, valves, sensors and boiler wear during use. The pump may fail because it is defective. This inevitably happens at the end of their life. This can happen unscheduled before the rated life if it is excessively stressed. So you have to watch the components states reguarly and exchange the worn components. In averge one could say you spend every year 550 Euro for interventions, but as you see, the costs scatter a lot over lifetime. Also the average for the intervention duration is calculated. Its about one day per intervention.
If there is not enough water inside the system the pressure can not be built up and the system fails. So the heating water has to be refilled from time to time. The combustion causes soot deposits in the boiler system. These settle in the gas or oil injection, more fuel is consumed and the required flow temperature is not reached. In the worst case, the injection clogs and the boiler no longer heats. Regular cleaning of all parts of deposits can prevent this. If the sensors are broken, the controller can no longer control the parameters such as flow and pressure. As a result, the boiler is loaded by thermal expansions. In the worst case, this can cause the boiler to rupture. By working on the heating system or leaks, air can enter the system. Important is a regular venting. The air in the system causes corrosion and flow noise and flow problems. In addition, most air bubbles form inside the radiator, resulting in a reduced radiating surface. If there is a leak in the pipe system, the pressure can not be built up. Such a leak may be caused by renovations, aging of the pipe sections (e.g. corrosion), or even frost damage due to insufficient insulation of pipes in the exterior walls. In addition, various valves may be broken. The valves after the radiator protect the pump from too much flow. This can break the pump. Therefore, the valves should be checked regularly for their function.
It can also be broken sensors or a wrong set up defined. The operating values always have to be checked and set in the right way. In the optimal case, the consequence of this is a fault condition, since the sensors warn of system damaging parameters and in the event of failure of this warning system, the system is turned off. If such a fault condition is not programmed, it can lead to defects on the other components.
So we see there are interventions necessary to keep the function of the heating system working.
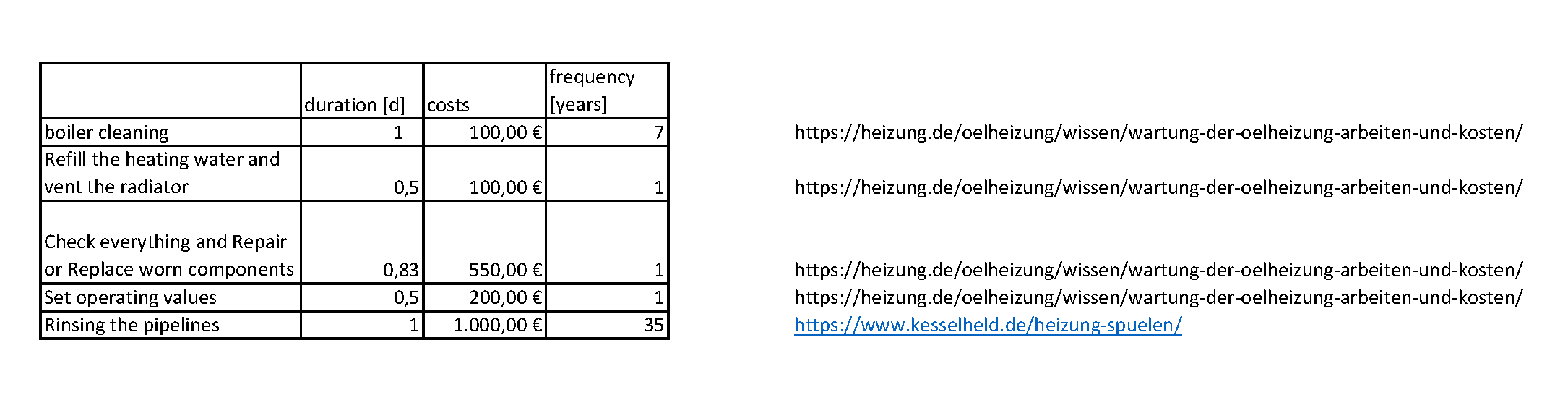
These are the middle values of duration, cost and frequency of the five important interventions we define for the heating system
The other civil engineering systems for the integrated system are a wind turbine and a multi-storey car park. All of these products are incorporated in overall maintenance strategies and are beeing assessed by a mulit- objective optimization.
[1] http://www.bosy-online.de/Nennlebensdauer.html
[2] https://heizung.de/oelheizung/wissen/wartung-der-oelheizung-arbeiten-und-kosten/
[3] https://www.kesselheld.de/heizung-spuelen/
[4] https://bvi-magazin.de/artikel/beheizte-rampen-und-einfahrten/
[5] https://www.kesselheld.de/freiflaechenheizung/