The functionality of a building depends on its accessibility, therefore, the core of successful planning lies in a coherent development concept. Elevators serve as vertical development elements and are indispensable for guaranteeing barrier-free buildings, as they allow the disabled and wheelchair-users access to all floors of a building. In the German „Musterbauordnung“, every building higher than 13 meters has to have at least one elevator and at least one elevator must be able to accommodate prams, wheelchairs, stretchers and loads.
Ontological Development
An ontology for an elevator system has been modeled into the program Protégé. The ontology follows a top-down development process which should help constructors, decide what kind of elevator they need for their object. The domain of the ontology is called “elevator” and its classes represents the types of elevators. As one can see in the following picture, the general super-classes are “function” and “drive type”, which are components of the elevator. Because of their dependency, they have the same taxonomic hierarchy. A rough sketch of the ontology follows:
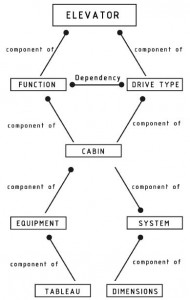
Following, the developed ontology in Protégé as a Super-link, as well as a visual representation:
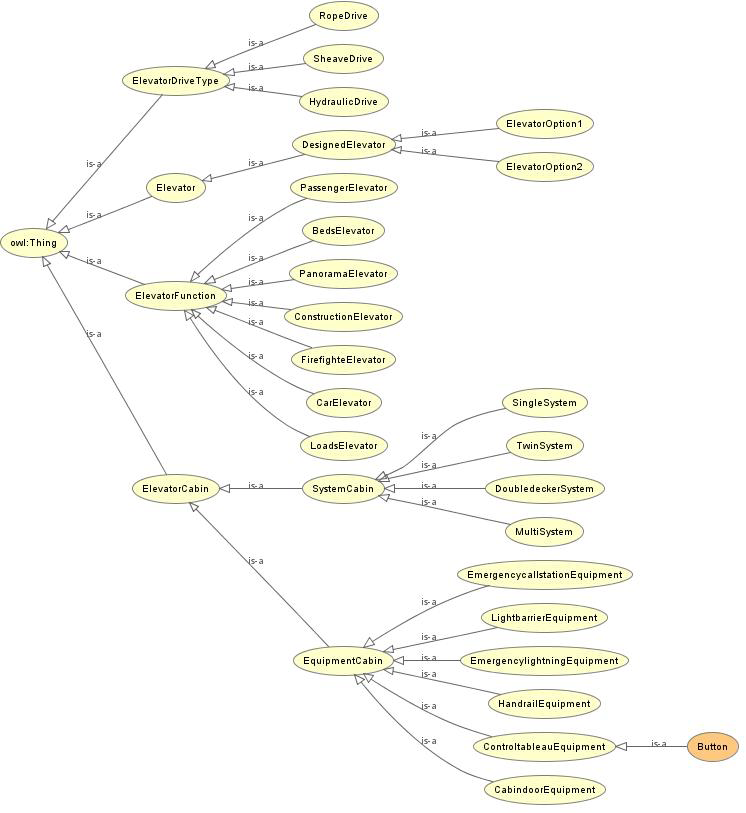
Parametric Model
After comprehending the main criteria and the high performance parameter of the elevator, a parametric model was developed using Dynamo, that geometrically visualizes the elevator. The challenge of the model is to provide different elevator sizes for different usages. The number slider of height, width and depth of the elevator are connected to all created elements. The most important decision that needs to me made during the planning of an elevator is the function, that the elevator needs to fulfill. Once the exact type of an elevator is defined, this parameter hardly changes. One specific challenge while designing a passenger elevator is finding the optimal size and bearing capacity for the given building situation. Since this model focuses on a passenger elevator, parameters with a high influence on the physical embodiment were selected
- Number of people using the building
- Utilization of the building
Apart from these parameters, the model is parameterised to have an influence on following criteria:
- Bearing capacity of the elevator (C)
- Width of the cabin (WC)
- Depth of the cabin (DC)
- Height of the cabin (HC)
- Width of the door (WD)
- Height of the door (HD)
- Coordinates for creating the axis
Following, the developed parameterised model in Dynamo as Super-link, as well as a visual representation: