Introduction of the System:
Developments in the construction of cut-off walls have enabled the construction of large zoned earth-fill embankment dams on deep foundations. In some cases, cut-off walls have also been used to rehabilitate aging structures. The primary function of a cut-off wall is to control or eliminate foundation seepage below dams from upstream to downstream. For dams that require a foundation cut-off, the cut-off wall is typically constructed in the foundation by the slurry trench method, then the dam is built on top of the cut-off wall and foundation [1].
Cutoff walls are often used in combination with other remediation and containment techniques such as pumping wells and gravity drains. The figure below shows an example of a hanging, down-gradient cutoff wall being used to stop the flow of a floating contaminant and a pumping well being utilized to remove the contaminant from the soil.
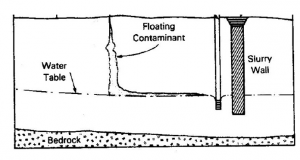 Figure 1: Cut Wall [2]
Figure 1: Cut Wall [2]
Boundary Conditions:
When conducting a life cycle analysis (LCA) and multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) for a cutoff wall, it is crucial to define comprehensive boundary conditions. For LCA, this involves assessing environmental impacts from raw material extraction to construction, operation, and decommissioning. In the context of MCDA, criteria include the cutoff wall’s effectiveness, environmental impact, technical feasibility, and adaptability. Evaluating the complete life cycle and various criteria ensures a holistic understanding of the cutoff wall’s environmental aspects, facilitating informed decision-making in its design, construction, and maintenance.
Life Cycle Analysis:
This function will take as input as following:
- Lifetime – Lifetime we assume for our civil system = 60 years
- Events – Events is a vector of interventions including the frequency of each
- M – Maintenance perform
I have chosen the material specifications and the environmental indicators according to the design options.
|
Design option |
Material | Material Specification |
|
Option 1 |
Geomembrane Cuttoffwall | Plastic Geomembrane (HDPE) |
| Option 2 | Concrete Cuttoffwall |
M25 mix IS code |
| Option 3 | Sheetpile Cuttoffwall |
Steel TMT 500 Grade 7.2 |
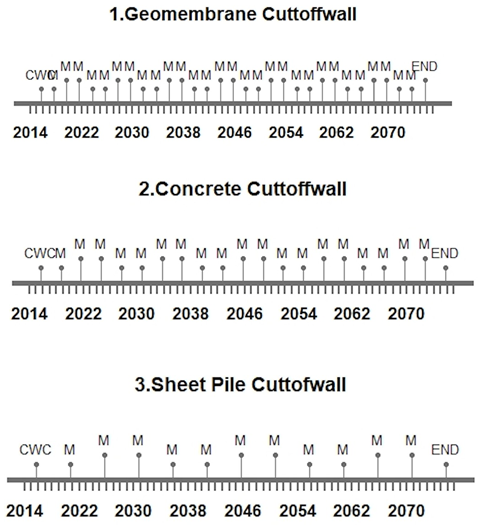
In this project, we have given three design options for the cutoff wall of the dam, from which we have analyzed that the use of concrete in the construction of a cutoff wall can emit more dangerous gases into the environment. In contrast, the use of a Geomembrane cutoff wall and Sheetpile cutoff wall emits less harmful gases into the environment. So it was recommended not to use concrete cutoffwall in dams. The timeline of all the Options is shown below:
Lifecycle inventory:
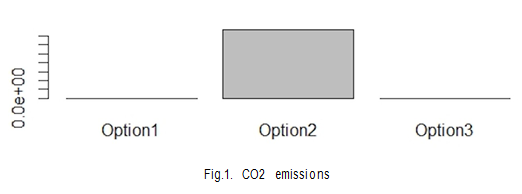
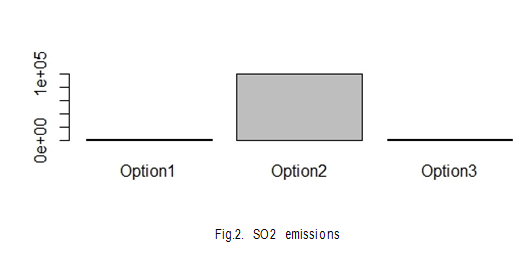
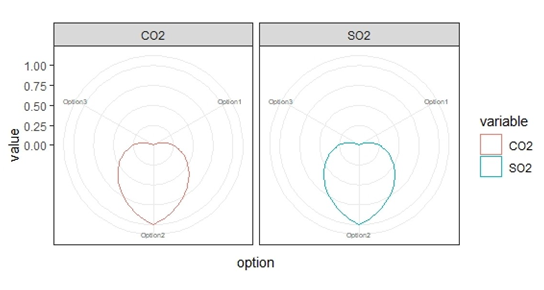
Bases on Dam’s dimensions and different design options for Cutoffwall, we will compute the total amount of emissions for CO2 and SO2.
It is clearly seen from the figure that design option 2 emits more CO2 than design option 1 and 3. The reason for this can be, the use of cement and other building materials used to make concrete.
This chart is generally used for showing comparison of the materials used here design option 2 has high emissions than the rest of the 2, from which we can say that the use of concrete in the construction of dams cutffwalls should be reduced in order to achieve higher environmental benefits.
Conclusion:
The Cutoffwall of Dam is the most essential component of Dam. It is the major component which is highly responsible for dams failures. It is used to control the seepage flow below the ground level, so it is necessary to select such materials which are durable and can withstand the seepage flow. Also, it becomes essential by which selection of cutoffwall material is not much harmful to the environment. In this project we have given three design options for cutoffwall of dam, from which we have analysed that the use of concrete in construction of cutoffwall can emit more dangerous gases into the environment. In contrast, the use Geomembrane cutoffwall and Sheetpile cutoffwall emits less harmful gases into the environment. So it is recommended not to use concrete cutoffwall in dams.
References:
[1] Quintal, D., & Otero, M. (2018). Vertical impermeable barriers (cutoff walls). Scribd. https://www.geoengineer.org/education/web-class-projects/cee-549-geoenvironmental-engineering-winter-2013/assignments/impermeable-barriers
[2] Hinchberger, S., Weck, J., & Newson, T. (2010). Mechanical and hydraulic characterization of plastic concrete for seepage cut-off walls. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 47(4), 461-471.