Introduction
Photovoltaic power plants convert sunlight directly into power. This type of power plant is considered a renewable option as the energy source is the sun, which is a clean, renewable, abundant, and cheap source.
Photovoltaic power plants consist of areas of panels of photovoltaic cells installed in an optimal configuration regarding their orientation and the angle of inclination.
These kinds of power plant tend to have the following basic components:
- Solar panels
- Support structure
- Investors to transform the DC into AC
- Batteries in case power storage is required
- Connection to the external grid or some kind of electrical load
PV Power Plants cover a wide range of output power, from 150W to several MW. This means it can be used for a large variety of purposes. Because of this, they can be installed in large fields as well as in available buildings roofs. In this last case, the foundations are not required and the support structure is supported on the building structure.
Ontological development
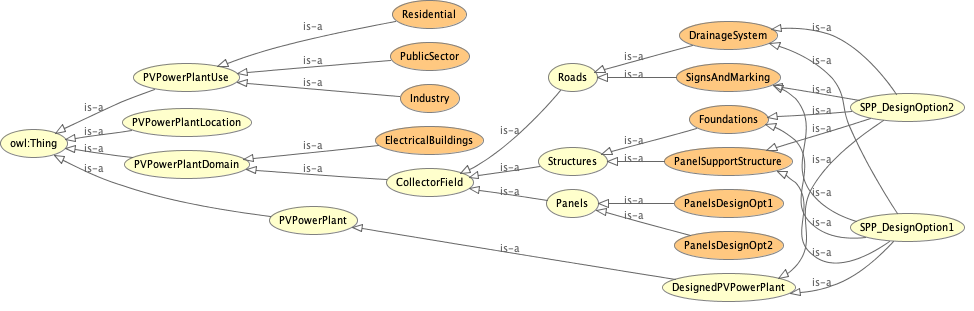
Photovoltaic plants can involve many different disciplines such as structural, geotechnical, hydraulic and electrical engineering. In relation to that, the location plays a key role when developing its design. Also, as mentioned before, they can be used for a wide variety of purposes and output required. Therefore and ontology is a helpful tool to have a clear understanding of the components of this system and it allows to analyze the relationship between them, with the aim to reach an optimum design and operation.
The visual representation of the ontology, for the more hierarchical levels, is shown in Figure 5 below:
Parametric model
The physical embodiment of the power plant is determined by parameters that allow exploring the design space and obtaining the optimum design and operation according to existing requirements or constraints.
These parameters are:
- Tilt angle (∅)
- Width of panels (x) and length of panels (y)
- The horizontal distance between supports (d)
- Height of supports to the foundations (clearance)
- Panels performance (W/m2)
High-performance criteria
It is essential to establish some high-performance criteria so that the performance of the design options can be measured and evaluated. For the photovoltaic power plant the high-perfromance criteria are listed below:
- Maximize the total power output generated (KW), as it can be storage and used for periods of lack of sunlight
- Minimize the total concrete volume (m3) to the aim of minimizing costs. For the integration of the systems, this HPC will not be considered given that the power plant will be located on the roof of the warehouse.
- Minimize the total weight of the metallic structure (ton) with the aim of minimizing costs.
- Achieve an optimal occupation of the field (%) to use as maximum panel rows as possible and therefore address the power output target.
In the following, the 3D model based on the described parameters shows the geometrical characteristics of the power plant: