Foundations are one of the most important elements of a structure, the purpose of which is to transfer the loads from the structure to the ground. Based on the use, soil condition, load from the structure, foundations can be classified and hence used accordingly.
-
ONTOLOGY OF FOUNDATIONS
- Purpose: The purpose of this ontology is to create a conceptual design of Foundations with a special focus on identifying the suitability of Foundations.
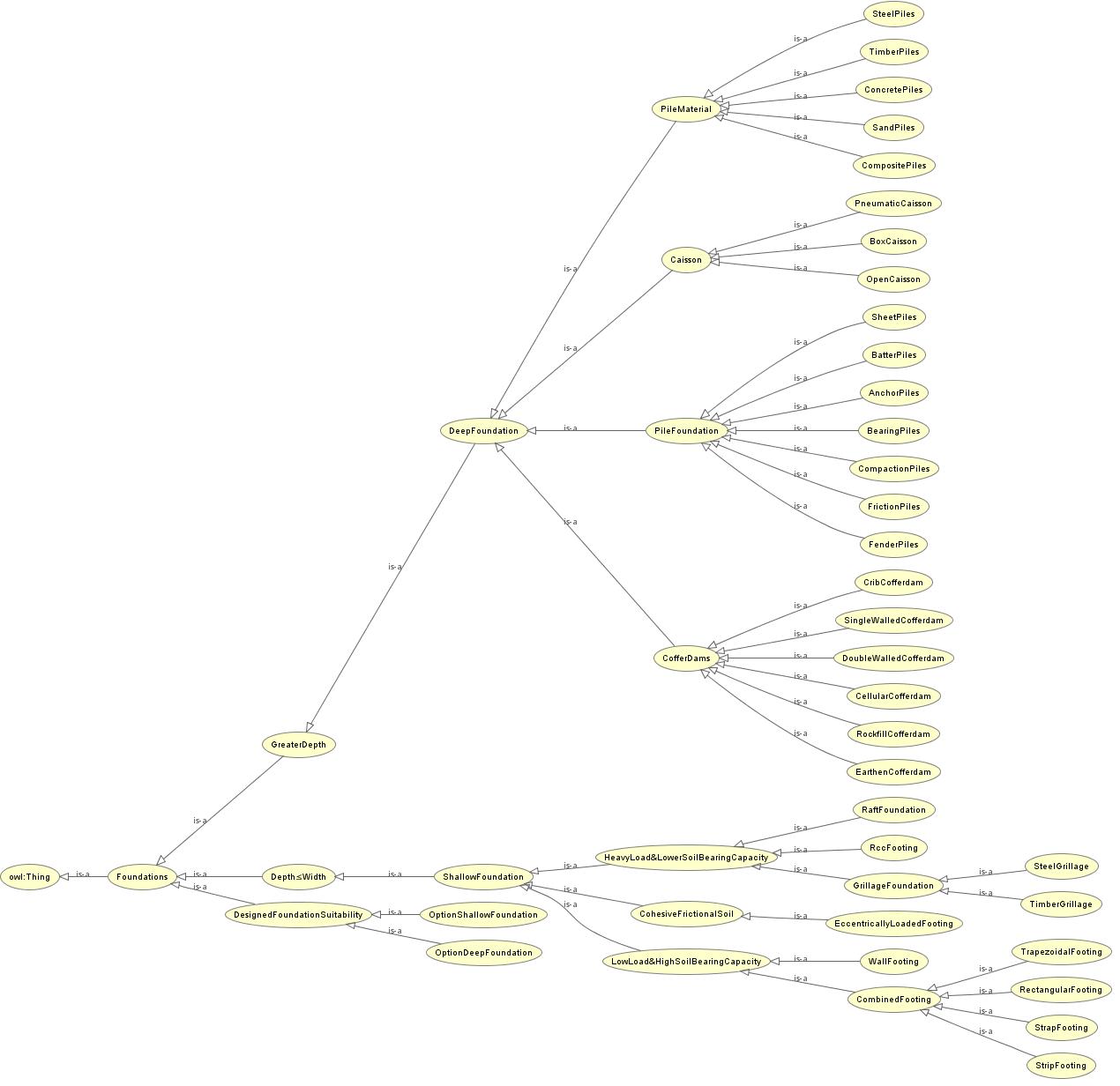
- Scope: This ontological model consists of a classification of foundations based on the Dimension relativity of a foundation (Depth and Width of the foundation) and the soil properties (Soil Bearing Capacity, Low Load, and Heavy Load Distributions) required to be adopted as a foundation for a structure under the given surroundings/ project site. It is classified based on the type of foundations, materials used, and their applications. This ontology helps in determining which foundation/footing is suitable under different circumstances that need to be adopted for a structure during the execution of the construction processes.
- Intended Users: The intended users are the Designers and the Engineers that are involved in the planning and design processes of a Foundation.
- Intended Use: This ontology can be used as a knowledge base for the basic conceptual design of a Foundation with identifying the suitable type under the parameters of foundation dimensions and soil properties as a focus. Since an extensive ontology requires a vast amount of time and huge knowledge, only basic concepts have been listed in this modeled ontology. However, this ontology can be further re-developed by inputting additional data and refining the same.
DEVELOPMENT OF AN ONTOLOGY
Resources [1, 2] have been referred to extensively in order to decide the classes and sub-classes used in the Foundations Ontology. A basic taxonomy of a few concepts that are important from the types, selection, and design point of view for foundations was created. Instances based on existing foundations have also been created. Based on the use, soil condition, load from the structure, foundations can be classified and hence used accordingly. Before commencing any construction project, the first advised work is to identify the suitability of the foundation for the particular structure. This ontological model helps in determining, identifying, and designing the same under the given circumstances that are to be adopted for the construction purpose.
An overview of all the classes and sub-classes considered is given in the figure below:
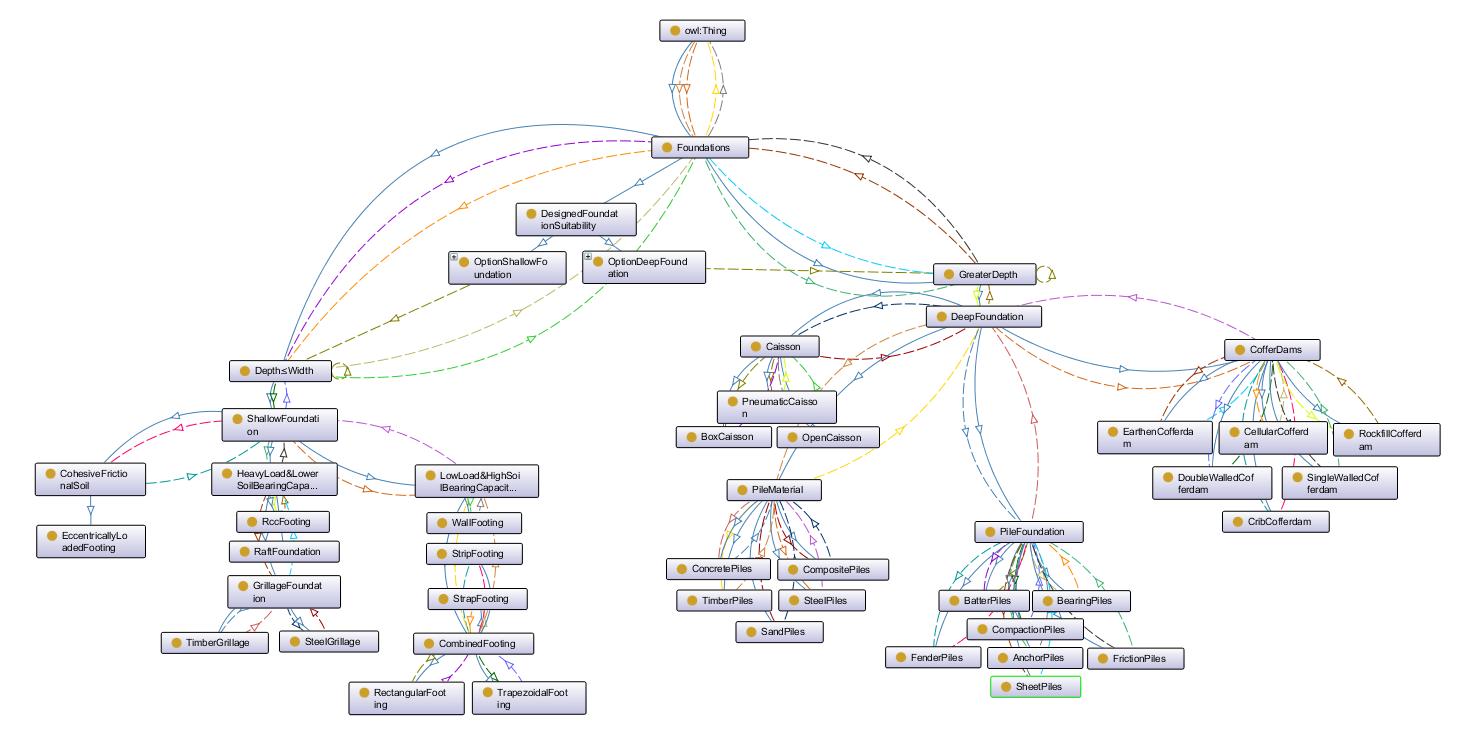
OntoGraf was created by protege for the developed ontology as depicted below:
-
PARAMETRIC MODEL OF FOUNDATIONS
[Resource 3] Parametric modeling is the creation of a digital model based on a series of pre-programmed rules or algorithms known as ‘parameters’ i.e., the model, or elements of it are generated automatically by internal logic arguments rather than by being manually manipulated.
It involves systematically and logically understanding the relationship between a number of important parameters of my engineering product, i.e., Foundations, its geometrical configuration and embodiment, and a set of high-performance criteria. parametric models allow for the very quick generation of possible design alternatives. Quicker generation, in turn, has the potential to allow us to quickly explore design spaces, find optimal solutions within these design spaces, and ensure that pre-given design constraints are accounted for.
- Design Challenge: For footings carrying heavy and unequal loads from two columns when the heaviest load outside the column distance has limited the area of footing is fixed and the soils at the site are loose soil.
- High-Performance Criteria: The parametric model developed helps in finding the suitable number, size of the footing required, and calculates the volume of the foundation for a defined number of lengths to increase the cost-efficiency. The High-Performance criteria for this assignment are to reduce the cost of foundation construction and find a suitable number of foundations over a stretch.
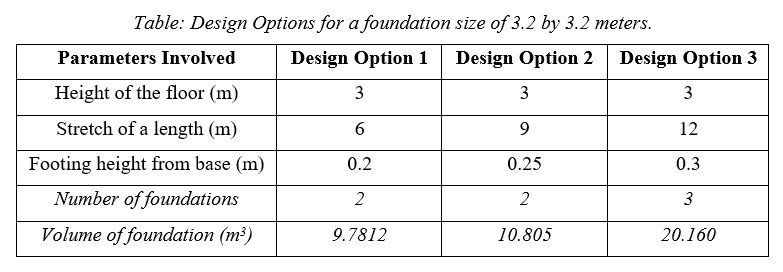
For High-performance criteria and high efficiency, the floor height is kept constant for 3 meters and three different Design spaces are stated in this report as best alternatives determined depending upon the three different sizes of the footing and at three different stretches of length.
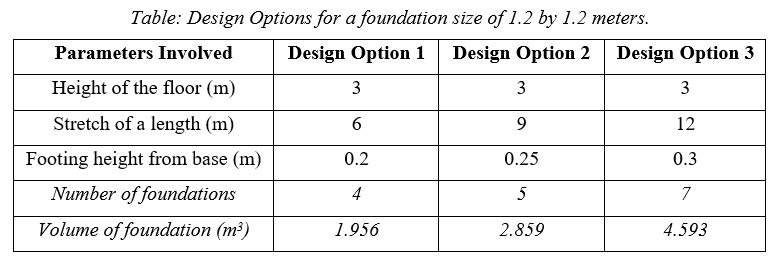
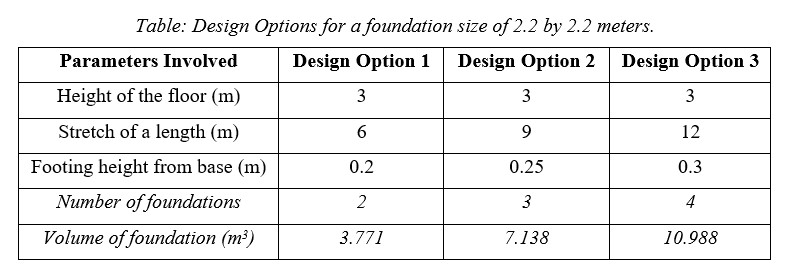
- [Resource 4] Based on the size and type of house and the bearing capacity of the soil, footing size can be recommended. Heavy houses on weak soil need footings 2 feet wide or more. But the lightest buildings on the strongest soil require footings as narrow as 7 or 8 inches. Under an 8-inch-thick wall, that’s the same as saying you have no footing.
- The cost of foundation depends on the volume of each isolated footing, number of isolated footings, the volume of tie beams, and cost of excavation. For High-performance criteria and high efficiency, the floor height is kept constant for 3 meters and three different Design spaces are stated in this report as best alternatives determined depending upon the three different sizes of the footing and at three different stretches of lengths.
RESOURCES.
[1] Mike Uschold & Michael Gruninger: “Ontologies: Principles, Methods, and Applications”.
[2] Natalya F. Noy and Deborah L. McGuinness: “Ontology Development 101: A Guide to Creating Your First Ontology”, Stanford University.
[3] Historic England (2019): “NB BIM for Heritage, Developing the Asset Information Model”.
[4] Concrete Network, Est. 1999: “Concrete footing size chart with standard widths”.