System Description
Our task was to integrate the three parametric models of a high-rise building in skeleton construction, a cable-stayed bridge, and a suspension bridge in a meaningful way. One could simply place the models side by side and adjust the parameters independently. However, this is not the goal of a combined model. Therefore, in this model, a scenario was created where the three models interact with each other, influenced by the two parameters: population and bridge length.
Scenario:
An adjacent city is expanding, and a satellite city is planned to be built on an island. The island has dimensions of 200 x 200 meters. The satellite city must be linked to the adjacent city by a bridge to facilitate the transport of commuters and goods.
Smart Choice of Bridge:
The bridge connecting the satellite city to the origin city can have its length adjusted. Depending on how far the satellite city is from the origin city, different types of bridges are more suitable. A cable-stayed bridge is the most economical for lengths between 550 and 1,000 meters. Only for longer spans will the more complex design of a suspension bridge be used.
Width of Bridge
The more people live on the island, the more car lanes the bridge will need. Therefore, the number of car lanes on the bridge will also be scaled according to the population. The function from the model of Bridge 1, which assigns a resulting bridge width based on the number of car lanes, bicycle lanes, and pedestrian paths, was applied to both bridges in the combined model.
Building Grid:
The Houses in the sattelite city are located in a 4 x 3 grid with one main street in extension of the bridge. The dimensions of the buildings can be chosen and the streets will still meet the required widths. The main street of the satellite island will now also be adjusted to the width of the bridge. The program ensures that a 5-meter front yard is maintained on both sides of the streets between the high-rise buildings, in addition to the required street width. In the side streets, there will be 25 meters between buildings, consisting of 15-meter-wide street cross-sections and 5-meter front yards on each side.
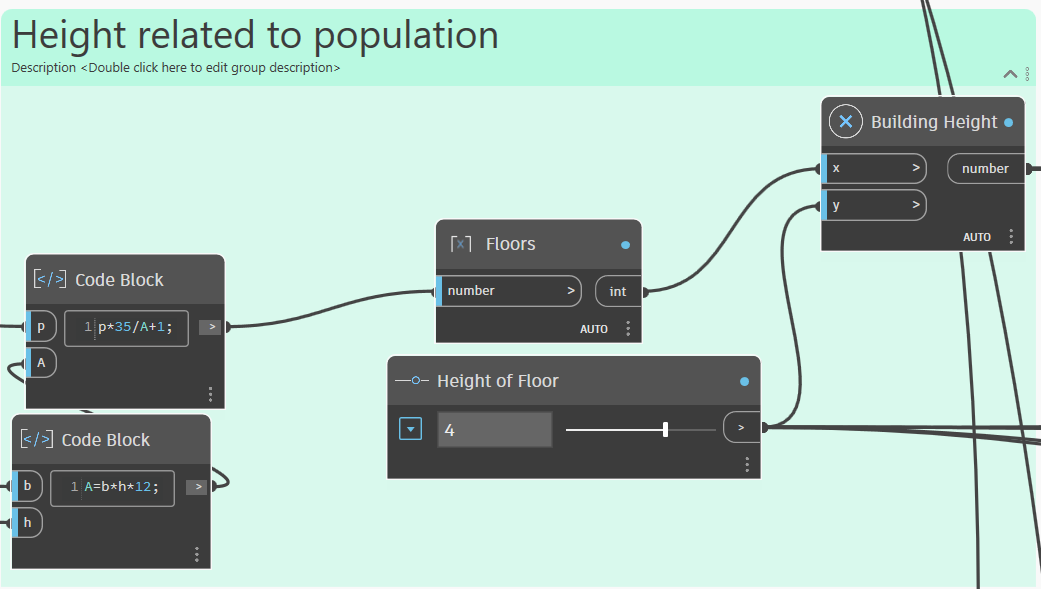
Building Height
Depending on the population size of the satellite city, the number of houses and floors will be automatically adjusted. On average, each person in the settlement is allocated a base area of at least 35 m², which is the higher average for compact city . This means the population was divided by the total base area of all 12 houses, and the result was rounded up to determine the number of floors. Additionally, one extra floor per house was reserved for commercial, educational, cultural, or social use.
Key Note : Challeneges Encountered – While merging the parametric model were the size of the merging big, the navigation at the beginning became confused. The software was slower because of the many commands of the merging of the different parameters of the models. Another challenge was moving three models starting from the same origin in the coordinate system.
Code for Height of the Building:
Two different Use Cases :
One possible configuration of the model is as follows:
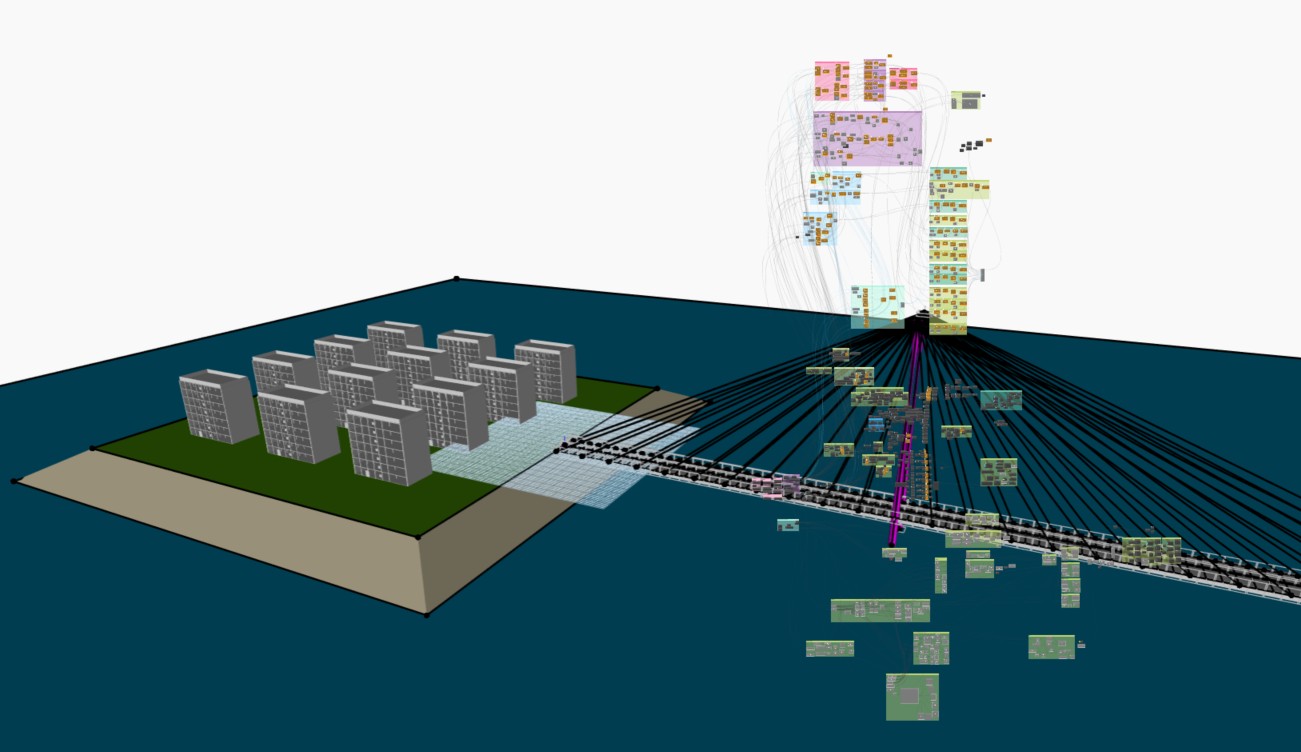
Population: 900
Building Width: 15 m
Building Length: 30 m
Heigth of Floor: 4.0 m
Length of Bridge: 700 m
Depth of Seabed: 12 m
Cables in Main Field: 28
Dynamo Workspace and 3D view :
Sketchfab View :
Another possible configuration of the model is as follows:
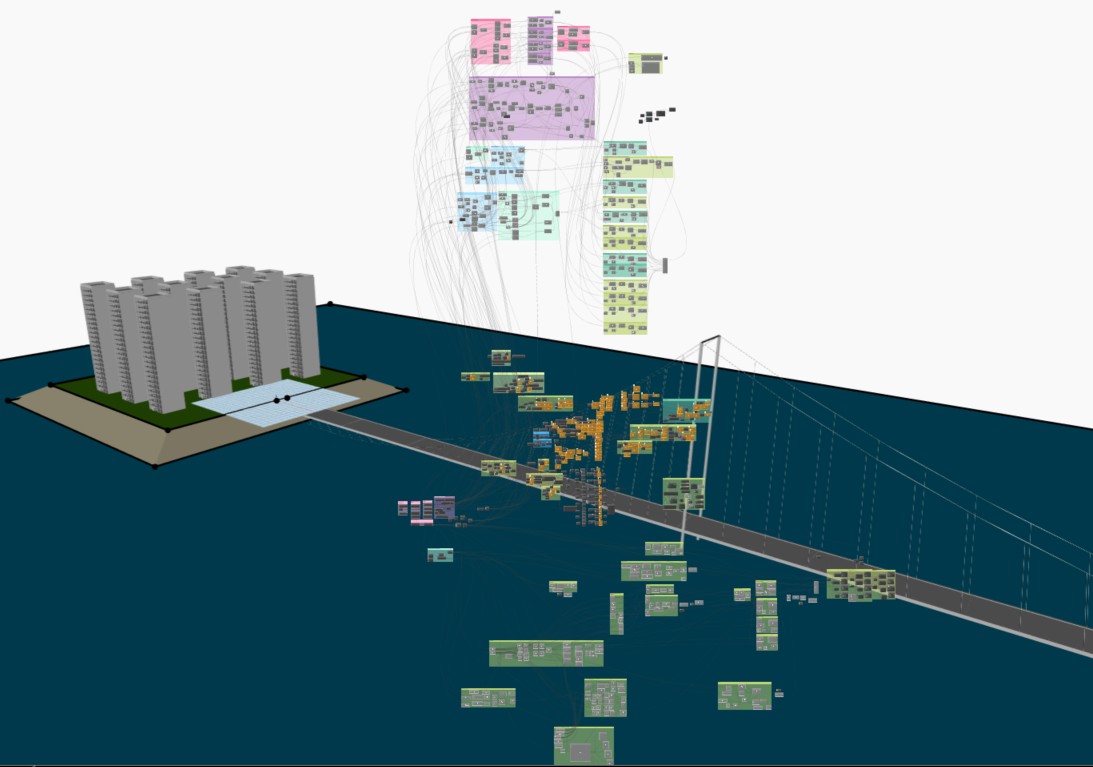
Population: 2900
Building Width: 20 m
Building Length: 20 m
Heigth of Floor: 4.0 m
Length of Bridge: 1500 m
Depth of Seabed: 14 m
Secondary Cables: 38
Dynamo Workspace and 3D view :
Sketchfab View:
| Main Page | Introduction | Individual Systems | Integration Context | Combined Ontology | Combined Parametric Model |