Introduction:
A dam is a structure built across a river or stream to hold back water. People have used different materials to build dams over the centuries. Ancient dam builders used natural materials such as rocks or clay. Modern-day dam builders often use concrete. Man Made dams create artificial lakes called reservoirs. Reservoirs can be used to store water for farming, industry, and household use. They also can be used for fishing, boating, and other leisure activities. People have used dams for many centuries to help prevent flooding.
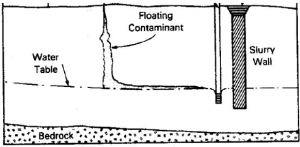
Developments in the construction of cut-off walls have enabled the construction of large, zoned earth fill embankment dams on deep foundations [3]. In some cases, cut-off walls have also been used to rehabilitate aging structures [2]. The primary function of a cut-off wall is to control or eliminate foundation seepage below dams from upstream to downstream [1]. For dams that require a foundation cut-off, the cut-off wall is typically constructed in the foundation by the slurry trench method, then the dam is built on top of the cut-off wall and foundation [2].
Figure: Cutoff wall, Pumping Well Combination for Remediation (USEPA, 1984)
Life Cycle Analysis
This function will take as input as following:
⦁ Lifetime – Lifetime we assume for our civil system= 60 years
⦁ Events – Events is a vector of interventions including the frequency of each intervention.
⦁ M – Maintenance perform
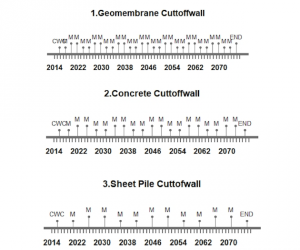
Timeline Graphs:
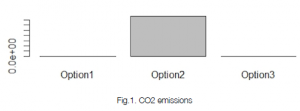
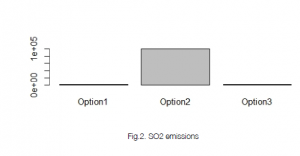
Emission Graphs:
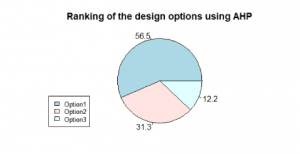
MCDA Chart:
Reference:
[1] Geomembrane Cutoff Wall Installation Utilizing a Narrow trench technique, XR Geomembranes (https://www.xrgeomembranes.com/projectprofiles/author/xr-geomembranes)
[2] Mechanical and hydraulic characterization of plastic concrete for seepage cutoff Walls, Article in Canadian Geotechnical Journal, April 2010
[3] Davidson, R.R., Levallois, J., and Graybeal, K. 1992. Seepage cutoff walls for mud mountain dam. In Slurry walls: design, construction