Parametric Model
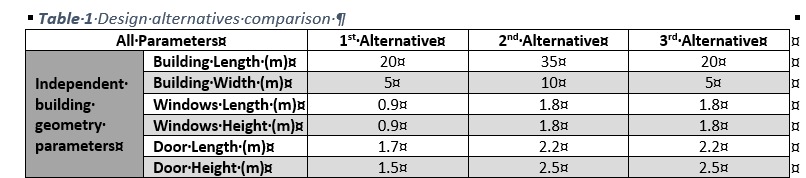
This study aims to investigate the heat loss through the building envelope in an aspect of parametric building modeling. In this context, a two-story residential building is chosen for a case study. The parametric relation between length and width of the building elements, that are used to calculate the area of them, are the fundamental geometrical configuration of building in this study. Subsequently, to calculate the heat loss through the building envelope (for energy performance), the thermal permeability values are the other important parameters. A two-story building is chosen for a case study. Firstly, the building geometry has been created along with cartesian coordinate and surface definition. After then, the area calculation has occurred. To calculate the heat loss through the building envelope (for energy efficiency), the thermal transmittance values are the other important parameters. This calculation was already calculated in the second assignment and does not appear here. Following the parametric model, three design alternatives are generated.
- The first alternative is that each parameter value is minimum.
- The second alternative is that each parameter value is maximum.
- The third alternative is that building geometry parameters (length and width of building geometry) are minimum whereas the geometry parameters for openings (windows and doors) as well as the thermal permeability values are maximum.
Consequently, the first alternative (among the others) is for the best design alternative of this study, due to having the small size building geometry for all elements and the lower thermal permeability values.
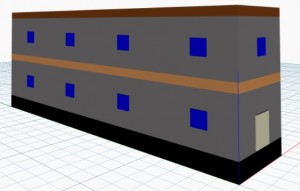
Figure 1: Residential Building
Decentralised Ventilation System | Virtual City Model